BIOS 1300 SI SI LEADER: MERRIN JEFFRIES (mj983011@ohio
advertisement

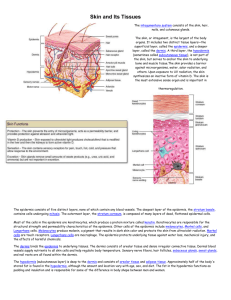
BIOS 1300 SI SI LEADER: MERRIN JEFFRIES (mj983011@ohio.edu ) WORKSHEET 6 (LAB EXAM 1/LECTURE EXAM 2 MATERIAL) 18 SEPTEMBER 2014 FILL-IN 1. Osteo means ______________; chondro means __________________________ . 2. Tendons, aponeuroses, elastic tissue and ligaments are all examples of ________________________________ . 3. The lining of the heart and blood vessels is called a(n) _____________________________________________ . 4. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is called an _________________________________ . 5. Neural tissue contains several kinds of supporting cells called ____________________________________________ . 6. The least specialized connective tissue in the adult body is __________________________________________ . Matching: Match the terms in column B with the terms in column A. Use letters for answers in the spaces provided. Use each term only once. ____________ 1. Serous gland A. tissue destruction ____________ 2.Holocrine gland B. movement of fluids ____________ 3. Fibrosis C. secretions released through exocytosis ____________ 4. Microvilli D. absorption ____________ 5. Cilia E. destruction of cell when secretions released ____________ 6. Merocrine gland F. watery secretions ____________ 7. Necrosis G. scar tissue ____________ 8. Gangrene part H. no blood flow that results in loss of a body Matching. Match the terms in the Key Choices with the statements listed below. Use each term only once. A. Adipocytes D. Elastic Fibers G. Matrix B. Chondrocytes E. Ground substance H. Reticular fibers C. Collagen fibers F. Macrophages _________ 1. Composed of ground substance and structural protein fibers. _________ 2. Clear, viscous fluid that fills spaces _________ 3. Tough protein fibers that resist stretching or longitudinal tearing. _________ 4. Fine, branching protein fibers that construct a supportive network. _________ 5. Large, irregularly shaped cells, widely distributed, often found in CT; they engulf cellular debris. _________ 6. Living elements found in the firm, flexible matrix in cartilage. _________ 7. Randomly coiled protein fibers that recoil after being stretched. _________ 8. In a loose CT, the nondividing cells that store triglycerides. The three types of muscle tissue exhibit certain similarities and differences. Insert SK (skeletal), C (cardiac), or SM (smooth) into the appropriate blanks to indicate which muscle type exhibits each characteristic. There may be more than one answer. ______ 1. Voluntarily controlled ______ 2. Contains spindle-shaped cells ______ 3. Involuntarily controlled ______ 4. Found in walls of small intestine, bladder and veins ______ 5. Banded appearance ______ 6. Contains long, nonbranching cylindrical cells ______ 7. Uninucleate ______ 8. Displays intercalated discs ______ 9. Multinucleate ______ 10. Nonstriated Identify the following structures or regions by labeling appropriate leader lines using terms from the list below: ______Tight junctions _____ Microvilli ______Epithelium _____ Capillary ______ Basal region _____ Connective tissue ______ Apical region _____ Basement membrane ______Desmosome _____ Cilia ______Nerve fibers _____Epithelial cell nucleus Multiple Choice. Circle the correct answer. 1. The two major cell populations found in connective tissue proper are: a. fibroblasts and fibrocytes b. mast cells and adipocytes c. melanocytes and fibroblasts d. fibrocytes and adipocytes 2. A fluid connective tissue found in the human body is: a. mucus b. blood c. areolar tissue 3. What type of connective tissue prevents muscles from pulling away from bones during contraction? a. dense irregular connective b. elastic connective c. dense regular connective d. collagen 4. Arrector pili muscles are associated with the: a. sebaceous glands b. sweat glands c. epidermis d. hair follicles 5.The primary tissues comprising the subcutaneous layer are: a. epithelial and neural b. transitional and glandular c. hyaline and cuboidal d. areolar and adipose 6. The terms merocrine and apocrine refer to two types of: a. ceruminous glands b. basement membranes c. sweat glands d. nails 7. Special smooth muscles in the dermis that, when contracted, produce “goose bumps” are called: a. tissue papillae b. arrector pili c. root sheaths d. cuticular papillae 8. Accessory structures of the skin include: a. dermis, epidermis, hypodermis b. cutaneous and subcutaneous layers c. hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands d. blood vessels, macrophages, neurons 9. An important function of the subcutaneous layer is to: a. stabilize the position of the skin in relation to underlying tissues b. provide sensation of pain and temperature c. adjust gland secretion rates d. monitor sensory receptors 10. Because freshwater is hypotonic to body fluids, sitting in a freshwater bath causes: a. water to leave the epidermis and dehydrate the tissue b. water from the interstitial fluid to penetrate the surface and evaporate c. water to enter the epidermis and cause the epithelial cells to swell d. complete cleansing because the bacteria on the surface drown 11. The protein that permits stretch and recoil of the skin is: a. collagen b. elastin c. keratin d. melanin 12. The dermis and epidermis are anchored to one another by ridges known as: a. dermal papillae b. gap junctions c. hypodermis d. melanocytes 13. Skeletal muscle fibers may be located in the: a. only the hypodermis b. dermis but not the epidermis c. epidermis but not the dermis d. neither in the hypodermis, dermis or epidermis 14. The primary pigments contained in the epidermis are: a. melanin and chlorophyll b. xanthophylls and melanin c. carotene and melanin 15. Bones forming the cranium and the scapula are referred to as: a. irregular bones b. flat bones c. short bones d. sesamoid bones 16. The bone of the cranium that exclusively represents single, unpaired bone in adult is: a. occipital, parietal, frontal, temporal b. occipital, frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid c. frontal, temporal, parietal, sphenoid d. ethmoid, frontal, parietal, temporal 17. At birth, the bones of the skull can be distorted without damage because of the: a. cranial foramina b. fontanels c. alveolar process d. cranial ligaments 18. The sinuses of the skull are found in the: a. sphenoid, ethmoid, vomer, lacrimal b. sphenoid, frontal, ethmoid, maxillary c. ethmoid, frontal, lacrimal, maxillary d. lacrimal, vomer, ethmoid, frontal Match the bone names listed in the key choices with the following bone descriptions. ______ 1. Connected by the sagittal suture A. ethmoid ______ 2. Cheekbone B. frontal ______ 3. Superolateral part of the cranium C. hyoid ______ 4. Contains the cribriform plate D. inferior conchae ______ 5. Posterior part of the hard palate E. lacrimal ______ 6. Posterior-most part of the cranium F. mandible ______ 7. Has two conchae as part of its structure G. maxillary ______ 8. Foramen magnum contained here H. nasal ______ 9. Site of the sella turcica I. occipital ______ 10. Houses hearing receptors J. palatine ______ 11. Forms the bone eyebrow ridges and roofs of orbit K. parietal ______ 12. Forms the chin L. sphenoid ______ 13. The only bone connected to the skull by a freely movable joint M. temporal ______ 14. Site of the mastoid process N. vomer ______ 15. Neither a cranial nor a facial bone O. zygomatic ______ 16. Tiny bones near the tear ducts ______ 17. Bony part of the nasal septum ______ 18. Anterior part of the hard palate