Notes Unit 3-4
advertisement
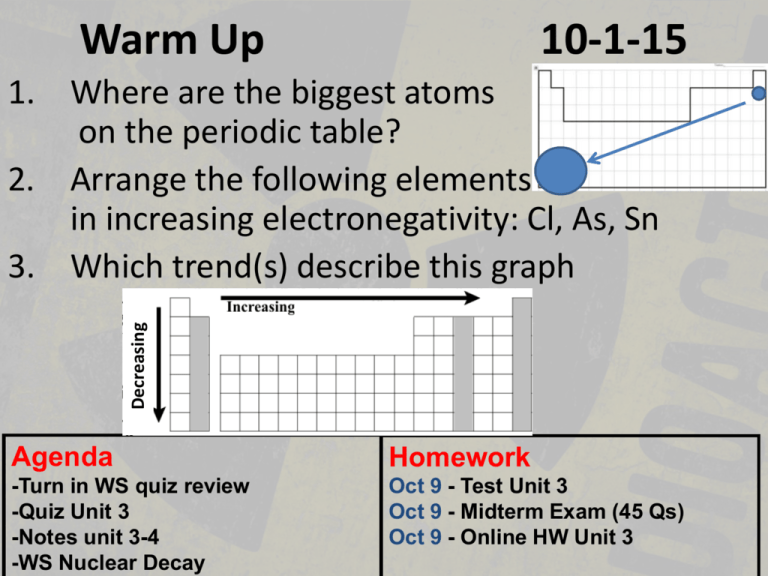
Warm Up 10-1-15 Decreasing 1. Where are the biggest atoms on the periodic table? 2. Arrange the following elements in increasing electronegativity: Cl, As, Sn 3. Which trend(s) describe this graph Agenda Homework -Turn in WS quiz review -Quiz Unit 3 -Notes unit 3-4 -WS Nuclear Decay Oct 9 - Test Unit 3 Oct 9 - Midterm Exam (45 Qs) Oct 9 - Online HW Unit 3 Quiz Unit 3 • You may write on the quiz • Unit 3-1 through 3-3 • 6 free response questions Unit 3-4 Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions Chemical Reactions: Atoms rearrange to form new substances, but atoms’ identities do not change. (electrons change, but nucleus remains the same) Nuclear Reactions: Chemical RxN that involves the changing of an atom’s nucleus. Large amounts of energy released compared to chemical reactions (mass defect) Nuclear Force • The nucleus is held together by residual strong force quarks & gluons transfer in the nucleus • Much stronger than the electrical repulsion between the protons • Stable nucleus have a ratio of 1 to 1.5 for neutrons to protons Radioisotopes • Radioisotopes- unstable isotopes that gain stability by releasing radioactive particles. α (alpha), β (beta), and γ (gamma) alpha Unstable isotope stable gamma beta Half-Life • Half-life is the time required for half of a radioactive substance to decay (to be stable). -20 g sample has a halflife of 5 years. How much is left after 10 years? 5g -How much is left after 3 half-lives? 2.5 g -After 4 half-lives how many percent is still radioactive? 6.25% • N-13 emits beta radiation with a halflife of 10 min. How long is three half lives? – 30 min • How many grams of the isotope will be left if there were 10 g of N-13? – 1.25 g Assignments • Summary • Question #16 ONLY on the worksheet today • Current event news article