1. D [1] 2. A [1] 3. (a) sodium/Na 1 (b) unclear correlation between V
advertisement
![1. D [1] 2. A [1] 3. (a) sodium/Na 1 (b) unclear correlation between V](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010240645_1-d92b6d492f0c376ebcb72250f62b109a-768x994.png)
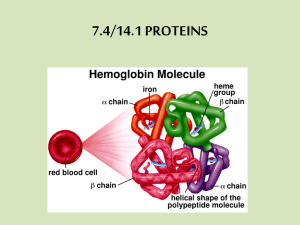
1. D [1] 2. A [1] 3. (a) sodium/Na (b) unclear correlation between V and T; depends on the nature of the substrate and its concentration; sometimes high V with low T (e.g. experiment 1 for sucrose) / sometimes high V with high T (e.g. experiment 2 for NaCl); 2 max higher salt/NaCl concentrations increase T and V; increase in puddling with increase in salt/NaCl; no clear relationship between the number of visits and the concentration of salt/NaCl; 2 max (c) (d) (e) (f) 1 (i) sodium/Na 1 (ii) retention of sodium/Na from laboratory solutions and natural puddles; definite loss of potassium from laboratory solutions but loss/gain uncertain from natural puddles; slight loss of magnesium from laboratory solutions and uncertain gain/loss from natural puddles; calcium uncertain in both cases / variation in data for calcium; more conclusive results in laboratory solutions / conditions more reliable in laboratory solutions / greater variation in natural puddles; Accept reference to error bars/ranges in data in place of uncertainty. 3 max males have longer/wider digestive tracts for greater absorption of fluid; ileum of males has greater surface area; which allows faster/more absorption in males than in females; 2 max puddling provides needed sodium/Na because their (larval) food does not supply enough sodium/Na; sodium/Na needed for neural activity; greater flight/neural activity in males than in females; Accept other reasonable suggestions. 1 max [12] 4. B [1] 5. A [1] 6. D [1] IB Questionbank Biology 1 7. D [1] 8. C [1] 9. A [1] 10. A [1] 11. (a) Fibrous protein: keratin / elastin / fibroin / collagen / myosin / actin / other named example; Globular protein: hemoglobin / myoglobin / named enzyme / named peptide hormone / named antibody / albumin / other named example; Example of both fibrous and globular protein needed to gain the mark. Check any other answers for validity. IB Questionbank Biology 1 max 2 (b) (c) both are polypeptides / chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds / have primary structure; globular proteins have tertiary structure whereas fibrous proteins do not (may have extended secondary structure); globular proteins are rounded in shape while fibrous proteins are elongated / OWTTE; globular proteins are (generally) soluble while fibrous tend to be insoluble; 2 max polar amino acids are soluble/have stable interactions in water/ extracellular fluid/cytoplasm; non-polar amino acids are soluble/have stable interactions in the lipid bilayer; polar amino acids strongly hydrophilic and non-polar amino acids are repelled by water/are hydrophobic; (help to) retain protein in position in the membrane; polar amino acids form hydrophilic channels/protein pores in membranes; transmembrane proteins have polar amino acids on either side of the membrane; 3 max [6] 12. C [1] 13. (a) (i) (ii) (b) primary structure is (number and) sequence of amino acids; joined by peptide bonds; secondary structure is folding pattern; held by H-bonds; α-helix / β-sheet; 3 max example of fibrous (e.g. collagen/myosin/keratin) and of globular (e.g. hemoglobin /myoglobin/catalase); fibrous are long, narrow shape while globular are rounded; fibrous are usually structural and globular are usually functional/ metabolic; fibrous are insoluble in water while globular are (usually) soluble; Award [1 max] if no example provided. 2 max oxidation is addition of oxygen while reduction is removal; oxidation is removal of H+, reduction is addition; oxidation is loss of electrons, reduction is gain; 1 max [6] IB Questionbank Biology 3