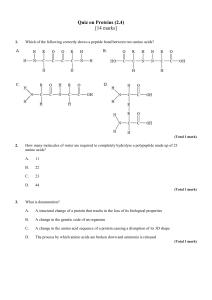
Four Functions of Proteins
advertisement

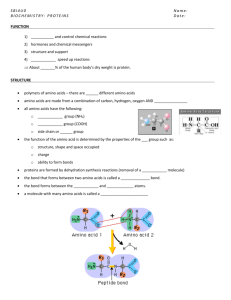
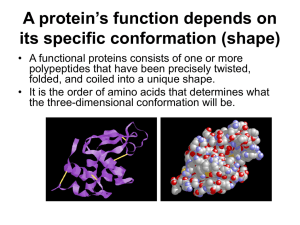
7.4/14.1 PROTEINS Protein’s have 4 levels of Structure: 1. Primary Structure = the order of amino acids that make up the polypeptide; amino acids are bonded together with peptide bonds What determines the order of amino acids? 2. Secondary Structure – the repeated, regular structures that polypeptide chains make due to hydrogen bonding; usually twisted alpha helices or beta-pleated sheets Alpha helix Beta pleated sheet 3. Tertiary Structure – 3D shape due to the bending and folding of the polypeptide; folds are the result of interactions between the R groups of amino acids bonds include covalent bonds (disulfide bonds between sulfurs), hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds ** folding occurs after translation 4. Quaternary Structure – when 2 or more polypeptide chains come together to make a protein; other elements may also be involved Prosthetic group Fibrous vs. Globular Proteins • Fibrous Proteins – long, narrow, and often insoluble in water – Ex: keratin – skin and hair – Ex: collagen – connective tissue – Ex: actin - muscles Fibrous vs. Globular Proteins • Globular Proteins – 3 dimensional and often water soluble – Ex: hemoglobin – Ex: insulin – Ex: enzymes – Ex: antibodies Significance of Amino Acid Polarity Non-Polar Amino Acids make up proteins that are typically hydrophobic and therefore found at inner parts of cell membrane, water insoluble Polar Amino Acids make up proteins that are typically hydrophilic and therefore found protruding through cell membrane; water soluble Enzyme-substrate specificity is also determined by polarity Review Question!!! What are the 6 functions of membrane-bound proteins? The 6 Functions Are… 1. Channel for passive transport 2. Pump for active transport 3. Hormone binding site 4. Enzyme 5. Cell to cell communication 6. Attachment Four Functions of Proteins: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Structure – collagen Movement – myosin and actin in muscles Gas transport – hemoglobin Defense – antibodies Enzyme – amylase Pick 4 to know! Hormone - insulin