Fibrous and Globular Protein
advertisement

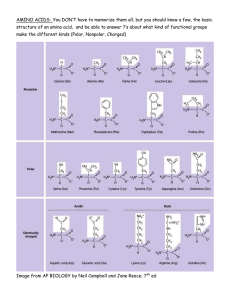
Presentation on Protein and Amino Acid Fibrous and Globular Protein Fibrous Protein • Proteins that is arranged in a long chain. • Typically water-insoluble, due to having the hydrophobic Amino Acids sticking out from the protein. • Most are Structural Protein, also acts as storage protein for energy and ions Examples • Collagen: Main structural protein in the human body, found in various parts of the human body, including muscles • Fibroin: Protein present in silk produced by some types of incest, including spiders • Keratin: Main structural protein in the outer layer of the human skin, also present in the nail and hair Globular Protein • Spherical shaped protein • Induced through the protein’s tertiary structure (Geometry of the protein) • More water soluble than Fibrous Protein, due to hydrophobic amino acid facing inward towards the center while hydrophilic amino acid facing outward Examples • Hemoglobin: Transport Oxygen around the human body • Actin: Used in muscle contraction • Antibodies (Immunoglobulin): Used in the Immune system to fight of diseases Polar and non-polar Amino Acid(AA) Peptide Polar Amino Acid • Peptides that have a Polar side chain • May include Oxygen or other polar functional group (etc. OH group) in the side chain • Includes AA like Tyrosine, Threonine, Serine and Asparagine Non-polar AA • Peptides that have a non-polar side chain • Mainly includes only carbon and hydrogen in the side chain • Includes AA like Alanine, Phenylalanine, Valine and Glycine. Charged AA • Amino Acids that have a side chain that can be charged • Depend on the pH of the solution and the pKa of the AA • Includes AA like Arginine, Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid and Lysine




![1. D [1] 2. A [1] 3. (a) sodium/Na 1 (b) unclear correlation between V](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010240645_1-d92b6d492f0c376ebcb72250f62b109a-300x300.png)