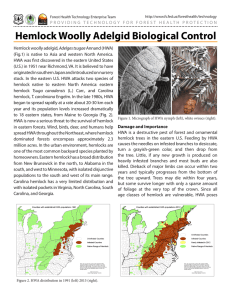
HWA CHONG INSTITUTION
Year One H1 and H2 Economics 2012
SELF-DIRECTED INDEPENDENT LEARNING PROJECT (ILP)
Report on the Self-Directed Independent Learning Project 2012
Group Members:
1.Cui Yi Mei
2.Yeo Chun Hui
CT: 12 S65
3.Wang Ye Chun
Complete the table below:
Role
Firm-
Audience
Monetary Consumers
Authority of Singapore
Form
Topic
Board Game: we will create a board game, with Monetary Policy
different scenarios, eg: economic recession,
conflict etc. Players will have specific amount of
money at first, on reaching different scenarios.
They may choose to borrow money from the
bank with the specific interest rate, as the
scenarios will affect the interest rate.
CONCEPT WRITE-UP
Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the
supply of money, targeting the rate of interest for the purpose of promoting economic growth
and stability by having relatively stable prices and low unemployment. There are two types of
monetary policy: expansionary or contractionary, where an expansionary policy increases the
total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual, and contractionary policy
expands the money supply more slowly than usual. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to
try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy
credit will entice businesses into expanding. Contractionary policy is intended to slow inflation
in hopes of avoiding the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values.
Monetary policy uses a variety of tools to influence outcomes like economic growth,
inflation, exchange rates with other currencies and unemployment. Where currency is under a
monopoly of issuance, or where there is a regulated system of issuing currency through banks
which are tied to a central bank, the monetary authority has the ability to alter the money
Hwa Chong Institution Economics Unit. All Rights Reserved. (Students’ copy)
HWA CHONG INSTITUTION
Year One H1 and H2 Economics 2012
SELF-DIRECTED INDEPENDENT LEARNING PROJECT (ILP)
supply and thus influence the interest rate to achieve policy goals.
Policy Goals:
High employment
Price stability
Economic growth
Interest rate stability
Financial market stability
Foreign exchange market stability
The expansionary monetary policy effects of lower interest rates also make bonds less
attractive than stocks and result in increase demand for stocks, which bids up stock prices.
Conversely, interest rate reductions make it cheaper to finance housing, causing real estate
prices to go up.
For example, when interest rate decreases, there is lower cost of borrowing, which results
in higher investment activity and the purchase of consumer durables. The expectation that
economic activity will strengthen may also prompt banks to ease lending policy, which in turn
enables businesses and households to boost spending. Lower interest rates also tend to cause
currencies to depreciate. Demand for domestic goods rises when imported goods become more
expensive. All of these factors raise output and employment as well as investment and consumer
spending. However, this stepped-up demand may cause prices and wages to rise if goods and
labor markets are fully utilized.
In Singapore, monetary policy is centered on the management of the exchange rate,
rather than money supply or interest rates. This reflects the fact that, in the small and open
Singapore economy, the exchange rate is the most effective tool in maintaining price stability.
Hwa Chong Institution Economics Unit. All Rights Reserved. (Students’ copy)
HWA CHONG INSTITUTION
Year One H1 and H2 Economics 2012
SELF-DIRECTED INDEPENDENT LEARNING PROJECT (ILP)
Hwa Chong Institution Economics Unit. All Rights Reserved. (Students’ copy)
HWA CHONG INSTITUTION
Year One H1 and H2 Economics 2012
SELF-DIRECTED INDEPENDENT LEARNING PROJECT (ILP)
My team’s 3 MCQs with justified solutions are as follows:
1.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Answer: (reason)
2.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Answer: (reason)
3.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Answer: (reason)
Hwa Chong Institution Economics Unit. All Rights Reserved. (Students’ copy)