Biology 1406
advertisement

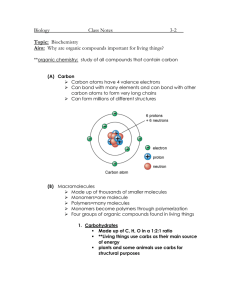
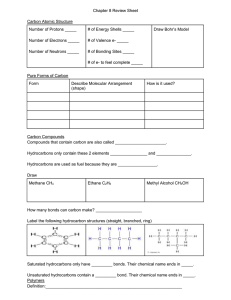
Biology 1406 Review Sheet for Exam 1 Mr. Dees Note: the following is a brief synopsis of the topics covered by the first lecture exam. Be sure that this sheet is not all that you study, for this list may be incomplete and is not very detailed. Anything covered in lecture is fairgame for the exam. Use this to be sure you do not have any “gaps” in your notes. A helpful section is provided at the end of each chapter in the form of a chapter summary, key terms, and review questions. Chapter 1 biology defined reasons why the understanding of biology is important 7 properties of living things with examples 7 themes of life Levels of biological organization with examples basic unit of life? prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells energy flow through living systems emergent properties feedback mechanisms biodiversity classification taxonomy Taxa(-on) Current taxonomic hierarchy binomial nomenclature three domains Evolution Darwin Natural Selection as a process Hypothesis and inquiry in science – scientific method Chapter 2,3,4 matter elements 92 natural, 25 essential to life CHON ? trace elements – with examples atoms subatomic particles and charge structure of atom molecules and compounds chemical bonds – energy? covalent bonds ionic bonds hydrogen bonds chemical reactions – components polar molecules vs. non-polar hydrophobic vs. hydrophilic properties of water specific heat cohesive, adhesive, vapor pressure, states, evaporative cooling electrolytes cations anions density of water vs. ice solvents solutes solutions universal solvent? pH scale acids vs. bases dissociation of HOH importance of C organic compounds vs. inorganic compounds carbon skeleton and functional groups and properties- function Chapter 5 macromolecules four categories of biological macromolecules polymers – monomers mechanism to build polymers dehydration synthesis –hydrolysis anabolic vs. catabolic reactions enzymes carbohydrates functions of carbohydrates monomers monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides – with examples and functions as discussed in class Glycosidic linkage Lipids no polymers!! all hydrophobic classes of lipids composition of fats (triglycerides) function of fats saturated vs. unsaturated fats phospholipid composition amphipathic molecules phospholipid bilayer steroids and examples Proteins many functions – know examples discussed in class amino acids – how many natural? components of amino acid peptide bonds what determines the function of a protein?? four level of protein structure denatured protein nucleic acids DNA and RNA components of nucleotide A,T, G,C, and U structure of DNA – double helix Watson and Crick genes phosphate-sugar backbone base pairs directional 3’-5’ antiparallel complementary strands replication RNA structure DNA and RNA at work