Active Transport - Bakersfield High School
advertisement

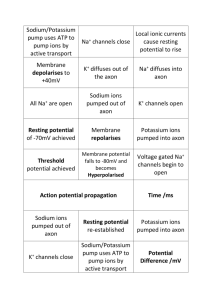
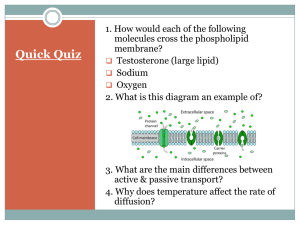
ACTIVE TRANSPORT Moving substances against their concentration gradient Cost energy!!! Types of Active Transport Sodium-potassium pumps Endocytosis Exocytosis SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMPS IN ANIMAL CELLS ONLY Moves 3 sodium ions out of the cell and brings in 2 potassium ions. Why? Prevents sodium from accumulating in the cell Maintain concentration of sodium and potassium across the cell membrane STEPS OF SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMP 1. 2. 3. 4. Three sodium ions inside the cell bind to the pump with an ATP. The pump changes shape to transport the sodium ions out. Two potassium ions bind to the pump outside of the cell. The potassium ions are transported into the cell and released. STOP- WATCH IT HAPPEN!!! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P-imDC1txWw ENDOCYTOSIS Movement of substances into the cell. 1. Cell membrane forms a pocket around the substance 2. The pocket closes up and pinches off of the membrane to form a vesicle. EXOCYTOSIS Movement of substances out of the cell Vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents Used by the cell to export proteins. STOP- WATCH IT HAPPEN https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DuDmvlbpjHQ COMPARE AND CONTRAST Compare and contrast active transport and passive transport.