Active Transport Webquest
advertisement

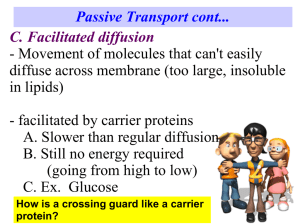
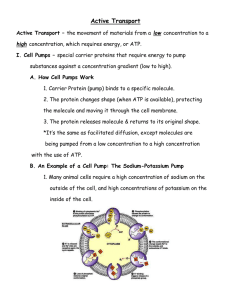
Name: ________________________________________________ Period: _____ Active Transport (chapter 7.4-7.5) Part I: Active Transport http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell2_activetran.html 1. What is active transport? 2. Why does the cell sometimes have to expend energy to move individual molecules across the cell membrane? 3. Which membrane molecules do most of the work in active transport? 4. Since these membrane proteins span the entire length of the lipid bilayer, what type of protein are they? 5. Membrane proteins are very __________________, meaning that they are designed to move only one or two types of molecules or ions across the membrane. 6. What does it mean by proteins working against a concentration gradient? 7. Sketch a diagram of active transport, showing the phospholipids and the proteins in the membrane. Also make sure to represent that the molecule is moving from low to high concentration. Part II: Endocytosis & Exocytosis http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120068/bio02.swf Play the animation to see an overview of endocytosis and exocytosis. 1. What are the three types of endocytosis? Summarize each. What does each type transport? 2. What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis? Part III: Na+/K+ Pumps One important type of ion pump that is responsible for the transmission of nerve signals is the sodium-potassium pump. http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/9834092339/student_view0/chapter44/sodiumpotassium_exchange_pump.html 1. What type of ions does the sodium potassium pump work with? 2. What are sodium potassium pumps responsible for in nerve cells? 3. Watch what happens in the animation and explain how a sodium potassium pump works.