Active Passive Energy needed?
advertisement

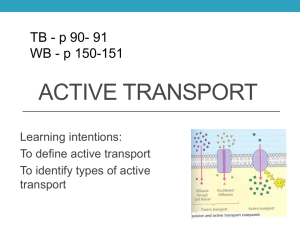
Quick Quiz 1. How would each of the following molecules cross the phospholipid membrane? Testosterone (large lipid) Sodium Oxygen 2. What is this diagram an example of? 3. What are the main differences between active & passive transport? 4. Why does temperature affect the rate of diffusion? Transport across membranesACTIVE DESCRIBE & EXPLAIN WHAT IS MEANT BY ACTIVE TRANSPORT, ENDOCYTOSIS & EXOCYTOSOIS Active vs. Passive Transport Active Passive Energy needed? Energy needed? Does not require E in the form of ATP Needs E in the form of ATP Active vs. Passive Transport Active Passive When If diffusion is not quick enough When To transport molecules across cell membrane high-low conc. To maintain homeostasis How does active transport help homeostasis? Example: Paramecium in fresh water 90% water 10% solute 99% water 1% solute How does active transport help homeostasis? Example: Paramecium in fresh water Contractile vacuole Pushes water Out of the cell How does active transport help homeostasis? Videos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pahUt0RCKYc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MPnXIvprb_w Active Processes Active Transport Bulk Transport What is active Transport? Which part of the membrane does this? Carrier Proteins-PUMPS! What direction is transport? Against the conc. Gradient (low-high conc.) What do they need to operate? Energy in the form of ATP Active Transport Carrier protein is a specific shape to fit a specific molecule Active pumps only pump each molecule in one direction. The Sodium Potassium Pump Most famous active transport in animals The sodium potassium pump This pump uses ATP to pump: 3 Sodium ions (Na+) out of the cell 2 Potassium ions (K+) into the cell Math example Sodium Potassium Pump Sodium Potassium Pump Movie https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fxOIcWwdl-o Why do cells do this? To lower salt concentration in the cell They are pumping more ions (salt) out than in, so the overall salt concentration stays lower This keeps it in balance with the outside environment To maintain an electrical charge in the cell This lets the cell get electrical signals from nerves Diagram it yourself With your partner, use your book on page 82 to diagram the four steps of the sodium potassium pump on a whiteboard. Be prepared to be called on to explain any part of the process. Bulk Transport-Moving large amounts Sometimes cells have to move really large molecules or objects into or out of cells Molecules like extra-large proteins or polysaccharides are too big to be transported even with the help of a protein The cell has to use bulk transport instead Endocytosis Bulk transport into a cell is called endocytosis. Steps First the membrane folds in to make a pouch. Then the objects to be transported enter the pouch. The pouch folds in on itself. Finally it pinches off to make a vesicle inside the cell. Exocytosis Bulk transport out of a cell is called exocytosis. Steps Cells package a molecule (like a hormone) into a vesicle. When the molecule is needed the vesicle goes to the cell membrane It fuses with the cell membrane and then opens up on the outside to let the molecule out of the cell Copy & complete the table Summary of transport Processes: Name of Description E Protein process of process needed? needed? Passive Processes Active Processes