Document
advertisement

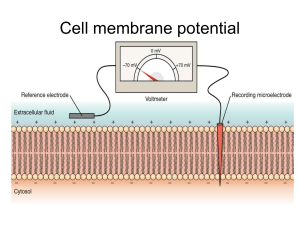
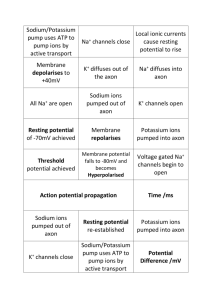
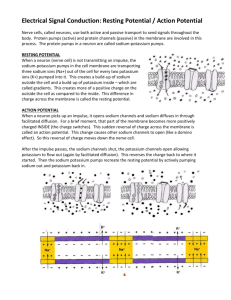
• ي Dr /Noha Elsayed Objectives • Define membrane potential, function and recognize steps of action potential . • Define conductivity and automaticity. • Characteristics of conduction in heart Is the difference in electric potential between the interior & the exterior of biological cells All eukaryotic cells maintain more negative charge in the interior than the exterior 1. Provide power to cells to operate their function 2. Used for transmitting signals between different parts of the body In all body cells, the membrane potential is held at relatively stable values in their baseline states called resting potential Opening & closing of ion channels ---- cause ions to pass from inside & outside the cell → leading to depolarization or hyperpolarization Depolarization Hyperpolarization If the interior is more positive If the interior is less positive Is an event in which the membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises & falls. Resting state Both sodium & potassium channels are closed & membrane is in resting state Depolarization phase Activation gates of sodium channels open, but potassium channels remain closed & so sodium ions rush into the cells leading to more +ve charge inside the cells Repolarization phase Back to resting state Inactivation gates close the sodium channels, but potassium channels open allowing potassium ions to leave the cells ---- leading to decrease in +ve charge inside the cell Automaticity (Autorhythmicity) Some tissues or cells have the ability to produce spontaneous rhythmic excitation without external stimulus. Different intrinsic rhythm of rhythmic cells Purkinje fiber, 15 – 40 /min Atrioventricular node 40 – 60 /min Sinoatrial node 90 – 100 /min normal pacemaker 11 Conducting System of Heart 12 characteristics of conduction in heart Delay in transmission at the A-V node (150 –200 ms) – sequence of the atrial and ventricular contraction – physiological importance Rapid transmission of impulses in the Purkinje system – synchronize contraction of entire ventricles – physiological importance 13 THANK YOU 14