Chapter 10 Common Exam Qs and MS
advertisement
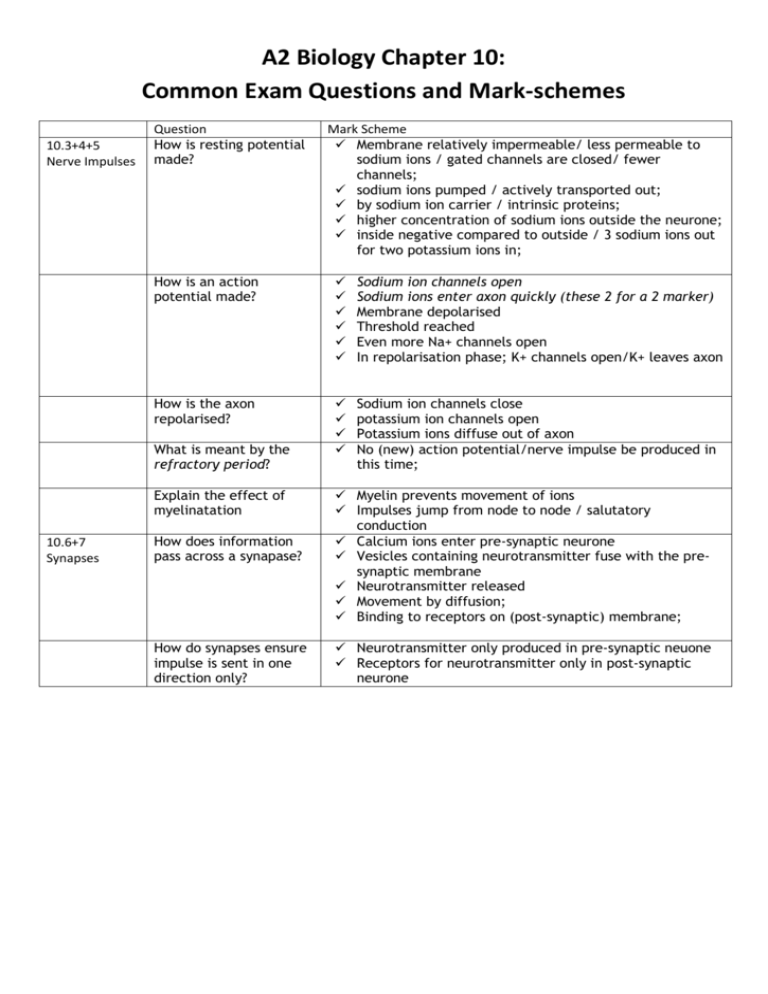
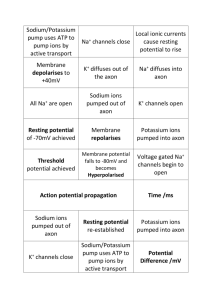
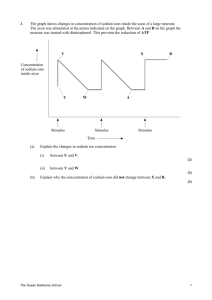
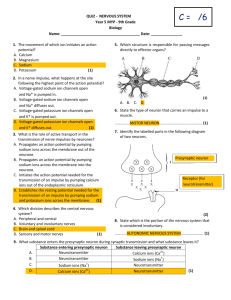
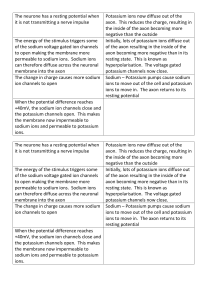
A2 Biology Chapter 10: Common Exam Questions and Mark-schemes 10.3+4+5 Nerve Impulses Question How is resting potential made? How is an action potential made? Sodium ion channels open Sodium ions enter axon quickly (these 2 for a 2 marker) Membrane depolarised Threshold reached Even more Na+ channels open In repolarisation phase; K+ channels open/K+ leaves axon How is the axon repolarised? Sodium ion channels close potassium ion channels open Potassium ions diffuse out of axon No (new) action potential/nerve impulse be produced in this time; What is meant by the refractory period? Explain the effect of myelinatation 10.6+7 Synapses Mark Scheme Membrane relatively impermeable/ less permeable to sodium ions / gated channels are closed/ fewer channels; sodium ions pumped / actively transported out; by sodium ion carrier / intrinsic proteins; higher concentration of sodium ions outside the neurone; inside negative compared to outside / 3 sodium ions out for two potassium ions in; How does information pass across a synapase? How do synapses ensure impulse is sent in one direction only? Myelin prevents movement of ions Impulses jump from node to node / salutatory conduction Calcium ions enter pre-synaptic neurone Vesicles containing neurotransmitter fuse with the presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter released Movement by diffusion; Binding to receptors on (post-synaptic) membrane; Neurotransmitter only produced in pre-synaptic neuone Receptors for neurotransmitter only in post-synaptic neurone