Reconstruction - Methacton School District
advertisement

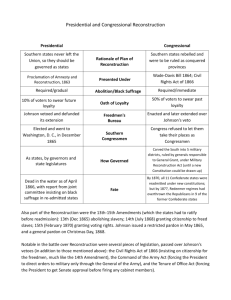
RECONSTRUCTION 1865-1877 Differing Meanings of Freedom • Freedom’s meaning to the former slaves • Open ended ideal based on equality and autonomy • Freedom’s meaning to former masters & white southerners • Mastery and hierarchy – a priviledge nota right • Most remained convinced that “the old relation of master and slave” had been the best condition in which the two races could live together for mutual benefit.” – Henry Ravenal, SC Planter • Freedom’s meaning to northern whites • Free labor – men were free to rise as far as the fruits of their labor would take them RECONSTRUCTION AMENDMENTS • 13th – Outlaws slavery and involuntary servitude • Adopted December 6th, 1865 • 14th – Section I, Section II-IV • Ratification bitterly contested. • ¾ ratification on July 9, 1868 • 15th - prohibits the federal and state governments from denying a citizen the right to vote based on that citizen's "race, color, or previous condition of servitude“ • Ratified Feb. 3rd, 1870 CHOICES FOR RECONSTRUCTION • How to treat states in rebellion • Conquered foe? • Who decides? • • • • Congress President Supreme Court Former Slaves? • Constitution is unclear Lincoln’s Second Inagural RECONSTRUCTION PLANS Moderate Republicans (Lincoln) • 10% Loyalty Oath • Win the South for Republicans Radical Republicans (Congress) • Radical Republicans (Congress) • 50% Loyalty Oath • Treat South as a conquered land FIRST STEPS • Freedmen’s Bureau • Assistance with food and legal questions • Schools • Sherman’s Example • 40 acres and a mule APRIL OF 1865 • Lincoln Assassinated • VP Andrew Johnson (TN) • Looked to follow Lincoln • Pro-Union, pro-states rights, racist, anti-slavocracy, proyeomen farmer • Personal plan more lenient • Johnson pushes it through Congress • Requirements • Renounce Confederate laws • Reject Confederate debts • Pass 13th Amendment Why might Lincoln choose to run with a southern slave owning senator for his second term? SOUTHERN REACTION TO LOSS • Black Codes • Paramilitary Groups • Election of former Confederates BLACK CODES • Enacted in 1865 • State by state • Attempted to reinstate slavery • Labor laws • Vagrancy laws The future of southern black codes Freed slave who refused to sign a labor contract is auctioned off to a white plantation owner who agreed to pay his fine – preference was often given to freedmen’s former masters KU KLUX KLAN • Established in 1865 in Tennessee • Spread throughout the South • Terrorist Intent • 10% of black office holders are known to have been victims of violent threats or assaults • At least 35 black officials murdered • Not a unified movement but one of many organizations • Suppressed in 1874 Confederate General Nathan Bedford Forrest ELECTIONS OF 1865 • Former Confederates elected and return to Congress • Former Confederate VP Alexander Stephens • Elected to the US House of Representatives 1873-1882 • Elected Governor of Georgia 1882 • Died March 4th,1883 NORTHERN REACTION AS COVERED BY HARPER’S WEEKLY NORTHERN RESPONSE • • • • Freedmen’s Bureau Bill (vetoed) Civil Rights Act (veto overridden) New Freedmen’s Bill (veto overridden) Elections give Republicans two-thirds majority General Oliver Otis Howard, Director of the Freedmen’s Bureau RADICAL (CONGRESSIONAL) RECONSTRUCTION • Begins after elections • Ignores President Johnson, turning back the clock to just after Appomattox • Reconstruction Act of 1867 (passed over veto) • Requirements • Allow blacks to vote • Pass 14th Amendment • Institute military governments Woodcut shows Freedmen’s Bureau agent separating armed whites from armed blacks. This image gives the impression that the Bureau was the only thing stopping a race war in the south during the period following Andrew Johnson’s failed reconstruction attempt. MILITARY RULE - 1867 • South divided into 5 military districts • Troops stationed in districts • Radical Republican state governments • Black participation in government A NEW SITUATION • Carpetbaggers (Northerners) • Scalawags (Southerners) ----------------------------------------• Resentment over the “Negro Rule” • Never actually happened • Two Senators & 15 Congressmen • South Carolina had black majority • Louisiana had a black governor NEW ECONOMIC STRUCTURE • Land Seizures Rejected • 40 acres and a mule • Sharecropping • Tenant Farming • Terms prevent independence • De facto (in fact) slavery IMPEACHMENT - 1868 • Johnson opposes Congressional will • Attempts to subvert Radical Reconstruction • Campaigns for Democrats • Misses removal by one vote RESULT • Johnson is marginalized • U.S. Grant elected in 1868 • Era of corruption (though not Grant personally) • North begins to lose interest in reconstruction The Meaning of Freedom to Freedmen • Family • Former slaves asked for help from the Freedman’s Bureau to help locate family members not seen in years and in some cases walked hundreds of miles to find former family members • Freedmen placed ads in newspapers seeking members of their family • Economic Independence • Land – the war over the economic resources of the South hardly ends with the end of shooting • Suffrage • “Slavery is not abolished until the black man has a ballot.” – Frederick Douglas • Access to Education • Beaufort NC first public school ever erected was built by freed blacks during reconstruction • Religious Autonomy • In the Front Street Methodist Church in Wilmington NC (which was 2/3 black) members told Reverend L.S. Burkhead that “his services were no longer required…he being a rebel.” 14TH AMENDMENT • Section 1. All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside. No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. 14TH AMENDMENT • Section 2 – Eliminated the Three-Fifths Clause • Section 3 – Banned Confederates • Section 4 – Removed War debt