File - Team 9 Titans
advertisement

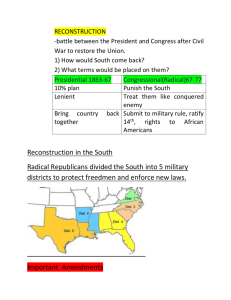
FRANCHISE AND NOT THIS MAN Thomas Nast Working for Harpers Weekly Reconstruction Chapter 3 How to reunite the nation? How to rebuild the South? What civil rights do African-Americans have? What does “all men are created equal” mean? – Today? – After the Civil War? I. Presidential Reconstruction (1863-1866) Abraham Lincoln 16th President Andrew Johnson 17th President A. Lincoln’s Plan (10% Plan) TO Rejoin the Union, a Southern state must: • 10% white Southerners must take a loyalty oath • New state constitutions must ban slavery • Amnesty given to most white Southerners who took oath BUT… . B. ASSASINATION – Abraham Lincoln is assassinated on April 14, 1865 – Many Northerners seek a greater CHANGE in South – President Johnson sets to battle with the Republicans of Congress Assassination of Lincoln http://www.glencoe.com/video_library/index_with_mods.php?PROG RAM=9780078777189&VIDEO=2593&CHAPTER=3&MODE=2 Confederates Punished? Alexander Stephens (Vice –President) • Arrested and held in prison for 5 months • Later elected to House and Governor of GA Jefferson Davis • Arrested and held in prison for 2 years • Moves to Canada but returns to Mississippi Captain Henry Wirz • Commander of Andersonville Prison (POW) • Executed for his crime of mistreatment Confederate Prison of Andersonville C. Andrew Johnson – Lincoln’s Vice-President (2nd term only) – A former Senator and a “War Democrat” from Tennessee (a Confederate state!) – A Southerner who remained loyal to the Union – Believes the wealthy planter class caused secession and the Civil War – Johnson’s plan is similar to Lincoln’s What about the FREEDMEN ??? II. Freedmen in Trouble (1865-1866) Freedmen and Sharecropping Freedmen Family near home Freedmen Family without a home Black Codes – Vagrancy leads to chain gangs II. Freedmen in Trouble (1866-1873) A. Black Codes 1. Laws made in Southern states to restrict freedmen’s rights AFTER the Civil War 2. Restricted property rights, arrested for minor crimes such as vagrancy and loitering 3. Not allowed to serve as witnesses and on juries Sharecropper (Tenant Farming) (1939) B. sharecropping (tenant farmer) – white landowner would rent a shack, land, seed and crude tools to tenant farmer – the tenant would pay landowner a “share” of the crop – the majority and the tenants lived in conditions worse than slavery What is going on here? What is going on here? What is going on here? What is going on here? What is going on here? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E4s2zl2trn0&feature=player_detailpage Ku Klux Klan Early disguises for Klansman Nathan Bedford Forrest “Wizard of the Saddle” C. Violence 1. Groups formed to intimidate freedmen like the Ku Klux Klan founded by Nathan Bedford Forrest 2. White population riots and attacks the freedmen in Memphis and New Orleans (1866) 3. Johnson does nothing to protect them III. Radical Reconstruction A. Congressional Leaders (“Radical” Republicans) 1. Thaddeus Stevens – Leader of House of Representatives from Gettysburg, PA – Hated slavery from his law work in Maryland 2. Charles Sumner – Leader of the Senate from Boston, MA – Beaten in attack in Senate in 1856 3. Benjamin Butler “the Beast" – Civil War general who “reconstructed” New Orleans – Elected in to the House and works for civil rights for freedmen Charles Sumner attacked in 1856 on the floor of the Senate What is going on here? B. HELP for the Freedmen 1. 13th Amendment – ends slavery 2. Freedmen’s Bureau (1865) • • • • • a federal agency created to help freedmen adjust to freedom Helped by providing food, clothing and medical services help get land and find work set up schools and academies Vetoed by President Johnson but is overridden 3. Civil Rights of 1866 • Granted full citizenship to African Americans • Bill is vetoed by Johnson but is overridden 4. CONGRESS V. PRESIDENT!!! C. Civil War Amendments • 13th Amendment (Jan 1865) • ends slavery • 14th Amendment (1868) • People born in the U.S. are American citizens • Citizens have rights • 15th Amendment (1870) • African-American males are given the right to vote African-Americans Voting Role of the Federal Government Carpetbaggers Andrew Johnson consulted General Ulysses S. Grant before selecting the generals to administer the military districts. Eventually he appointed John Schofield (Virginia), Daniel Sickles (the Carolinas), John Pope (Georgia, Alabama and Florida), Edward Ord (Arkansas and Mississippi) and Philip Sheridan (Louisiana and Texas). D. Reconstruction Act of 1867 1. Radical Republicans pass new law: • • • • Southern states divided into 5 military districts Guaranteed rights of African-Americans to vote Banned Confederate leaders from holding office Required army to REGISTER voters and protect freedmen 2. To rejoin nation, Southern states had to: • Ratify the 14th Amendment • Submit new constitutions for Congressional approval E. Johnson’s Impeachment 1. Congress pass laws to weaken president 2. Tenure of Office Act of 1867: - Forbid president from removing officials without Senate approval 3. House of Representatives IMPEACH Johnson in March 1868 for removing Secretary of War 4. Senate held a TRIAL three days later - Senate acquitted president (voted not guilty) by one vote Edmund Ross - Radical Republicans were one vote away from 2/3 majority Impeachment & Trial of President Johnson IV. President Ulysses S. Grant A. Election of 1868 1. Ulysses S. Grant (R-OH) v. Horatio Seymour (D-NY) 2. 3. Grant wins a landslide in the electoral college voting Main issue: Reconstruction and Free Labor Grant Seymour Election of 1868 Grant (R) 52.7% popular vote 214 electoral votes Seymour (D) 47.3% popular vote 80 electoral votes Red = Republican won state Blue = Democrats won state B. Grant’s Reconstruction Policy 1. Supports military protection of the freedmen by using the “Force Acts” 2. Support Radical Reconstruction policies to help rebuild the South C. Corruption 1. Scandals • Credit Mobilier Scandal (1872) » Company uses bribes to get favorable railroad contracts in the West • Whiskey Ring (1875) » Tax money is “funneled” illegally to whiskey distilleries 2. “Carpetbaggers” and “Scalawags” • Southerners link corruption to the Northerners and Republicans in their states III. Reconstruction - Successes A. African Americans Political Leaders • 16 African-Americans elected to House of Representatives • Senator elected Hiram Revels and Blanche K. Bruce (see p88) • Never gained control of state governments • Very few African-Americans have been elected president (1), governor (4), and Senator (7) African American Congressmen B. Education 1. The Freedmen’s Bureau Schools – Established primary schools • 50% white & 40% black children attended • Schools were segregated – Most teachers were from the North 2. Academies – Specialized schools to train skills – develop into “Black Colleges” such as Fisk (WEB Dubois), Howard (Thurgood Marshall) & Morehouse (Martin Luther King) – http://www.infoplease.com/ipa/A0872606.html Freedman’s School Education Graduates from “Black Colleges” IV. Failure of Reconstruction – “The Redeemers” A. How did “White Power” get control in South? 1. Amnesty Act of 1872 • Law PARDONS almost ALL white Southerners • All pardoned could VOTE and HOLD OFFICE • Democratic Party in South regains power of state governments (by using majority voting, trickery or terrorism) 2. Election of 1872 • Republican party divides over corruption • Grant defeats Horace Greeley (Liberal Repubican) • Republicans begin to move away from Reconstruction and focus on the economy Election of 1872 Grant (Red) v Greeley (Blue) Republicans 286 Lib Rep/Dem 63 3. Panic of 1873 (Panic is another word for Economic Depression) • Thousands of businesses close and tens of thousands of Americans lose jobs • Republican leaders blamed for the economy 4. Election of 1876 a. Rutheford B. Hayes (R) v. Samuel Tilden (D) b. Tilden wins the popular vote BUT No CLEAR WINNER in electoral vote c. Electoral College dispute in three Southern States d. Congress awards all 20 elector votes to Hayes making him president e. Hayes makes deal to end “Radical” Reconstruction and to pull army out of the South Rutherford B. Hayes Samuel Tilden Election of 1876 Hayes 165* Tilden 184 (*All 20 disputed Electoral Votes awarded to Hayes given him the needed 185 to win) V. Legacy of Reconstruction Which would you like to use? A. Divided Society (Segregation) 1. “Reedemers” seize control Southern States – Goal is to end the Republican control of their state governments 2. Demorcats want to restore “White Power”: a. Conservative Fiscal Policy • Cut state spending • lower taxes • end funding to schools and for social policies b. Voting Restrictions – Poll tax, literacy test, & the Grandfather clause c. Jim Crow Laws – Laws that created a segregated society in public places till 1965 – “White” and “Colored” division in schools, restaurants, transportation, etc… B. Constitutional? 1. Local police ignore the abuse of freedmen 2. Plessey v Ferguson (1896) - Supreme Court rules that the concept of “separate but equal” as constitutional 3. Civil Rights movement fights to end segregation in 19501960s 4. Brown v. Board of Education (1954) - Supreme Court OVERTURNS and rules that “separate but equal” as UNCONSTITUTIONAL Legacy of Reconstruction Change is not welcomed Change is NOT easy! Change? http://www.gilderlehrman.org/multimedia #3337