Chapter 22 - Twinsburg Schools
advertisement

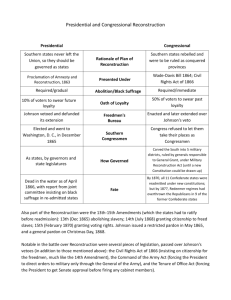
Chapter 22 The Ordeal of Reconstruction 1865-1877 Questions after the War • • • • • • How would the South be rebuilt? What about the new freedmen? How do we bring the South back to Union? Who was in charge of Reconstruction? Jefferson Davis Southern devastation destroyed infrastructure • “The lost cause” Charleston, South Carolina, in Ruins, April 1865 The Freedmen’s Bureau • Freedmen’s Bureau March 3, 1865 • Union General Oliver O. Howard • Intergenerational education • Corruption of Bureau Educating Young Freedmen and Freedwomen, 1870s Presidential Reconstruction • Lincoln’s 10% Plan (1863) • Congress counteracted with Wade-Davis Bill (1864) pocket vetoed • 2 factions in Congress- Radical and Moderate Republicans • Johnson’s Reconstruction ProclamationMay 29, 1865 Black Codes • November 1865 Black Codes in Mississippi • White control subservient population • Labor force (Cotton Kingdom) contracts signed for 1 year service • Few rights • Created generations of sharecroppers • North= what did we fight for? Congressional Reconstruction • December 1865: new Southern members of Congress (ex Confederates!) • Fear of Democrat take over • Black population= whole person, more power to South! • February 1866: Johnson vetoed Freedmen’s Bureau extension • Republicans in Congress= Civil Rights Bill Congressional Reconstruction • Future Congress might undo Civil Rights Bill- needed 14th amendment • Citizenship rights to blacks • Reduced representation of state if black voting denied • Denied office to former Confederates who had sworn to uphold US Constitution before • Repudiated Confederacy’s debts • 1866 midterm elections= veto proof Republicans Congressional Reconstruction • Radicals= Charles Sumner (Senate), Thaddeus Stevens (House) • Saw South as conquered provinces • Use federal power to revolutionize • Moderates= more states rights, ensure citizen rights with little federal intrusion Military Reconstruction • Reconstruction Act March 2, 1867 • South= 5 military districts (martial law) • Readmittance to Union= ratify 14th amendment, guarantee black voting in state constitutions • Usurped President’s power as commander in chief • Ex parte Milligan case • Needed 15th Amendment to ensure Southern compliance • Return to “Redeemer” governments (Solid South) Military Reconstruction, 1867 (five districts and commanding generals) Freedmen Organization • Lincoln and Johnson= gradual suffrage • Moderate Republicans unsure of 15th amendment many Northern states denied voting to blacks • Union League formed • Civic education, black schools/churches, militias • Universal manhood suffrage 14 Congressmen/ Senators between 1868-1876 Angry White South • “Scalawags”: white Southerners helping new regimes (Republicans) thieves • “Carpetbaggers”: white Northerners who came to South for personal profit • New regimes reformed system • KKK formed in Tennessee 1866 • Terrorism to “put blacks/white Republicans in place” • Force Acts of 1870 and 1871 The Ku Klux Klan, Tennessee, 1868 Johnson Impeachment • Too many clashes with Congress wanted to replace him with Ben Wade of Ohio (president pro tempore) • Tenure of Office Act 1867 • Fired Secretary of War Edwin Stanton • Impeached by House 126 to 47 Senate heard case for removal • Johnson’s argument avoided removal by 1 vote • Precedent? Purchase of Alaska • Russia wanted to sell Alaska 1867 • Secretary of State William Seward bought for $7.2 million • “Seward’s Folly” • Didn’t want to offend Russia, future economic opportunity?, flank GB Alaska and the Lower Forty-eight States (a size comparison) Reconstruction- Failure? • Too difficult to change South socially, politically, racially • No clear picture of what Reconstruction should have been from beginningpiecemeal • Black rights soon denied for over 100 years • Too much desire for white dominance vs. not enough desire to force South