Reconstruction and Redemption
advertisement

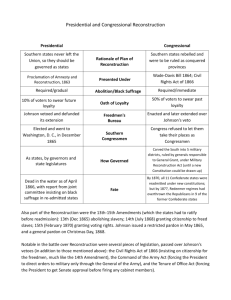
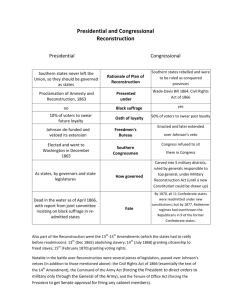
CHAPTER 22 THE ORDEAL OF RECONSTRUCTION For the South: A Tale of Ruin ● Economic Devastation Charleston, South Carolina (1865) • destruction of labor force • end of plantation system • infrastructure ruined • extreme poverty • source of wealth (slaves) erased • land values plummeted • hyperinflation due to worthless currency ● Social Changes • destruction of planter aristocracy • 1/5 of all white males dead For the North: A Different Story ● Economic Opportunity ● rebuild the South with northern free labor ideology ● invest in southern infrastructure (especially RR) ● help the South industrialize ● “carpetbagging” ● Social Opportunity ● educate southern blacks ● bring the South into 19th century with abolition and a more egalitarian society ● Political Opportunity????? Presidential Reconstruction vs. Congressional Reconstruction Lincoln’s Plan ● Lincoln’s hope ● wanted to re-establish southern loyalty ● bring confederate states back into Union ● end the war quickly ● 1863 Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction ● ● ● ● 10% plan of full pardons restored rights for all southerners willing to take oath to the U.S. (Confed. officers, high rankers excluded) abolition must be accepted before re-admission no provisions to overturn black codes, little protection for social equality, no economic aid or the franchise for blacks The Wade-Davis Bill in Opposition to the “10% Plan” 50% oath of allegiance Stronger safeguards for emancipated slaves Vetoed (pocket veto) by Lincoln When Congress reconvenes, they refuse to seat some southern delegates who followed Lincoln’s plan Radicals wanted the South to atone for its sins (they committed “state suicide”) and could only come back as conquered states Johnson’s 10% Plan (upon the untimely death of Lincoln) Johnson’s Proc. of Amnesty and Reconstruction (1865) Delivered when Congress was out of session for the summer Pardoned most Southerners Pardoned Confed. officers, high-ranking officials if they applied for personal amnesty (which most did and received) Once oaths taken and former slaveholders pardoned, states could convene to write a new constitution and send it to Johnson for approval Radical Republicans’ (Sumner, Stevens) Plan Wanted South to slowly integrate back into Union (which party dominated the South pre-Civil War?) Protect the right of blacks to vote and form a political base Blacks then could gain more basic rights as the South accepts abolition Reconstruction Act (1867) Passed by a veto-proof Congress South must accept 14th & 15th Amend. before readmission Until then 5 military governors would rule 5 districts to enforce the black vote and equality All orders from the Pres. to army went through General Grant (who supported Radical Reconstruction) 50% loyalty oath (Confed. officers barred from office and vote) Still no land or educational guarantees (moderate Republicans were not in favor) Radical Republicans Continued 13th (1865): abolish slavery 14th (1868): citizenship and equal protection under the law Why is this necessary? What happened about 10 years earlier? 15th (1870): the right to vote Freedmen’s Bureau (1866) Emergency agency to assist transition for freedmen and white refugees Distributed clothing, food, and fuel, established schools Civil Rights Act (1866) : precursor to 14th Amend. Vetoed and overridden Gave all persons born in U.S. citizenship with full set of civil rights (suing, testifying, due process) Can you tell why a white Southerner might hate the Freedmen’s Bureau? The Impeachment of Andrew Johnson • The Radical Congress had been challenging Johnson’s “Reconstructed South” since Dec. 1865 • Alexander Stephens (the vice-President of the C.S.A.) was elected to Congress! • Johnson is charged with violating the Tenure of Office Act (1867) • President cannot remove Senate-approved officials w/o Senate approval • Impeachment trial for “high crimes and misdemeanors” in Feb. 1868 (avoided by one vote) for firing of Secretary of War Stanton In the Newly Reconstructed South New state constitutions helped elect blacks A new tax system financed public schools, infrastructure improvements and public works Some of this was done under the guidance of carpetbaggers and scalawags that were corrupt As states were readmitted, federal troops withdrew “Redeemer” Democrats emerged (known as conservatives) The KKK is born in 1866 Black codes (soon to be known as Jim Crow laws) rolled back any legal or social gains Sharecropping replaced slavery