File
advertisement

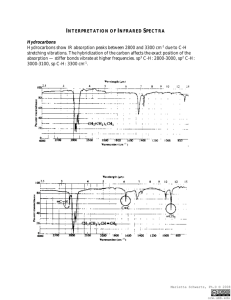
1 O-H and N-H Stretching • Both of these occur around 3300 cm-1, but they look different. – Alcohol O-H, broad with rounded tip. – Primary amine (RNH2), broad with two sharp spikes. – Secondary amine (R2NH), broad with one sharp spike. – No signal for a tertiary amine (R3N) 2 Alcohols have characteristic IR absorptions associated with both the O-H and the C-O stretching vibrations. •O–H stretch, hydrogen bonded 3500-3200 cm-1 and is a very intense, broad band •C–O stretch 1260-1050 cm-1 (s) 3 An Alcohol IR Spectrum => 4 Amines The N–H stretches of amines are in the region 3300-3000 cm-1. (weaker and sharper than alcohol O–H stretches). -In primary amines (RNH2), Secondary amines (R2NH) show only a single weak band , only one N–H bond. -Tertiary amines (R3N) do not show any band in this region since they do not have an N–H bond. 5 6 7 8 9 Stretching vibrations (Carbonyl groups) Structural unit Range, cm-1 Aldehydes and ketones 1710-1750 Carboxylic acids 1700-1725 Acid anhydrides 1800-1850 and 1740-1790 Esters 1730-1750 Amides 1680-1700 C O 10 Aldehydes and ketones A useful diagnostic band for aldehydes is the O=C–H stretch, in the region -1 2800-2700cm . 11 12 13 14 Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids show a strong, wide band for the O–H stretch. Unlike the O–H stretch band observed in alcohols, the carboxylic acid O–H stretch appears as a very broad band in the region 3300-2500 cm-1, centered at about 3000 cm-1. This is because carboxylic acids usually exist as hydrogen-bonded dimers. O–H stretch from 3300-2500 cm-1 C=O stretch from 1700-1725 cm-1 15 O-H Stretch of a Carboxylic Acid This O-H absorbs broadly, 2500-3500 cm-1, due to strong hydrogen bonding. 16 17 Esters 18 19 An Amide IR Spectrum 20 A Nitrile IR Spectrum 21 1-Explain which functional group is present in the compound with the following IR spectrum. Show to which class these compounds belong. 3100 -- The broad intense absorption band seen here is characteristic of a carboxylic acid dimer. 2960 -- CH aliphatic stretch 2870 -- CH aliphatic stretching. 1720-- CO 22 The compound is aliphatic carboxylic acid 3080 -- Aromatic CH absoprtion 2760 -- Aldehyde CH 1735 -- C=O absorption 1615 -- The 1600 and 1500 bands for the aromatic nucleus are variable. The compound is aromatic aldehyde. 23 2995 --Aliphatic CH stretching vibration absorption. 1765 & 1740 -- C=0 Note the two minima of this band. Two carbonyls. 1045 -- Symmetric strectch for the C-O-C of the ester. The compound is aliphatic ester 24 3350 -- The broad intense absorption band seen here is characteristic of -OH 2950 -- CH aliphatic stretch ------- no C=O absorption The compound is aliphatic alcohol 25 2229 3080 -- Aromatic CH absoprtion 2950-2850 -- CH aliphatic stretch C N 2229 -The compound is aromatic nitrile substituted with alkyl group 26 1716 2900-2850 --Aliphatic CH stretching vibration absorption. 1716 -- C=O absorption No other absorption Simple aliphatic ketone 27