polyatomic ions - Salem Community Schools
advertisement

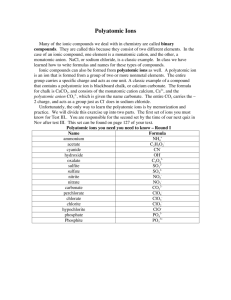
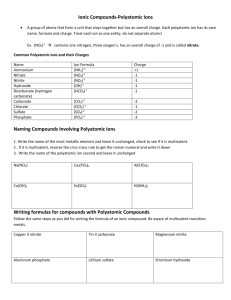
POLYATOMIC IONS Two or more atoms covalently bonded, the resulting particle has a charge. Many polyatomic ions are listed on the back of your periodic table. Other polyatomic ions are on page 224 of your textbook. Look at the list on the back of your periodic table. When the polyatomic ion has a negative one charge, it wants to gain one electron. On your worksheet, list the polyatomic ions that want to gain one electron. What would be the charge of a polyatomic ion that wants to gain 2 electrons? -2 Now find the polyatomic ion with a positive charge, it is called ammonium. NH4+1 The positive charge means it wants to lose an electron. Let’s look at sulfate… An atom of sulfur has 6 valence electrons. An atom of oxygen also has 6 valence electrons. When you put 4 oxygen atoms with 1 sulfur atom, you get a structure that looks like this…… Notice how the one oxygen does not have a complete octet, it wants to gain two more electrons for an octet. This is why the sulfate ion has a negative 2 charge. Practice When given a formula, you know it contains a polyatomic ion if it has more than 2 elements. Use your periodic table and write the name of the following on your worksheet. ZnCO3 NaNO3 K2SO4 NH4Br Practice Hopefully you got the following: ZnCO3 NaNO3 K2SO4 NH4Br Zinc(II) carbonate Sodium nitrate Potassium sulfate Ammonium bromide Practice a few formulas Lithium phosphate Aluminum carbonate Barium hydroxide Iron(III) acetate Hopefully you got these: Lithium phosphate Aluminum carbonate Barium hydroxide Iron(III) acetate Li3PO4 Al2(CO3)3 Ba(OH)2 Fe(C2H3O2)3