Document
advertisement

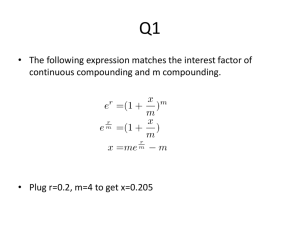
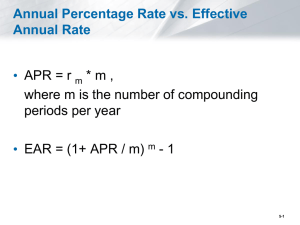
Investment Analysis Lecture 4 Complications in NPV Investment Analysis Complication 1 Inflation How does inflation affect DCF analysis? CF1 NPV = CF2 + (1+r) CF3 + CF4 + CF5 + +… (1+r)2 (1+r)3 (1+r)4 (1+r)5 Discounting Rule Treat inflation consistently: Discount real cash flows at the real interest rate and nominal cash flows at the nominal interest rate. Investment Analysis Complication 1 (cont’d …) Terminologies Cash flows Nominal Real = = Actual Cash Flows Cash Flows expressed in today’s purchasing power Real CFt = Nominal CFt / (1 + Interest Rate)t Discount Rates Nominal Real = = Actual Interest Rate Interest Rate adjusted for Inflation 1 + Real Interest Rate = (1 + Nominal Interest Rate) / (1 + Inflation Rate) Real Interest Rate = [(1 + Nominal Interest Rate) / (1 + Inflation Rate)] - 1 Investment Analysis Example This year you earned $100,000. You expect your earnings to grow about 2% annually, in real terms, for the remaining 20 years of your career. Interest rate is currently 5% and inflation rate is 2%. What is the present value of your income? Investment Analysis Complication 2 Compounding Frequency On many investments or loans, interest is often charged or credited more than once a year. Examples Bank Accounts – Daily Mortgages and Leases – Monthly Bonds – Semiannually Implication Effective Annual Rate (EAR) can be much different that the stated Annual Percentage Rate (APR). Investment Analysis Compounding - Consider investing $100 at the annual interest rate 10%. How much will your investment value in 3 years? > After 1 year you will have: $100 x 1.1 = $110 > After 2 years you will have: $100 x 1.12 = $121 > After 3 years you will have: $100 x 1.13 = $133.1 - This is different from $100 + $30 = $130 - Have to account for interest on interest. - More generally, investing C dollars at the annual interest rate r gives, C ( 1 + r )t dollars after t years. Investment Analysis APRs & EARs Habib Bank quotes you a rate of 7% for your home mortgage. The mortgage involves monthly payments. • 7% is not the “true” annual rate, it is only used to derive the monthly rate by: x = 7% / 12 = 0.583% • The “true” annual rate is: (1 + x)12 – 1 = 7.23% • 7% is the Annual Percentage Rate (APR). It is the quoted rate. • 7.23% is the Effective Annual Rate (EAR). It is the true rate. Investment Analysis APRs & EARs : Compounding Frequencies Example: Suppose your bank offers a 1-year CD with a 5% APR, what is the EAR with; • • • • • • Annual Compounding? Semiannual Compounding? Quarterly Compounding? Monthly Compounding? Daily Compounding? Continuous Compounding? 1.05 (1+ 5%/2 )2=1.050625 (1+ 5%/4 )4=1.050945 (1+ 5%/12 )12=1.051161 (1+ 5%/360 )360=1.01267 Lim (1+ 5%/T )T=… T ∞ General Formula: with T compounding periods in a year APR EAR = ( 1 + )T - 1 T Investment Analysis APRs & EARs (cont’d …) Example Car Loan ‘Finance charge on an unpaid balance, computed daily, is at the rate of 6.75% per year. If you borrow $10,000 to be repaid in one year. How much would you owe in a year? Daily Interest Rate = 6.75 / 365 = 0.0185% Day 1: balance = 10,000 x 1.00185 = 10,001.85 Day 2: balance = 10,000 x (1.00185)2 = 10,003.70 ……….. ………………………………………………………………… Day 4: balance = 10,000 x (1.00185)360 = 10,698.50 EAR = 6.985% Investment Analysis Complication 2 (cont’d …) Discounting Rule In applications, interest is compounded at the same frequency as payments. If, so just divide the APR by number of compounding intervals. Bonds Make semiannual payments, interest compounded semiannually, discount semiannual cash flows by APR / 2. Mortgages Make monthly payments, interest compounded monthly, discount monthly cash flows by APR / 12. Investment Analysis Complication 3 Currencies How foreign currency cash flows are discounted? CF1 PV = CF0 + CF2 + (1+r) CF3 + (1+r)2 CF4 + (1+r)3 +… (1+r)4 Discounting Rule Discount each currency at its own interest rate: discount $ at the U.S interest rate, discount € at the european interest rate. This gives of PV of each cash flow stream in its own currency. Convert to domestic currency at the current exchange rate. Investment Analysis Currencies (cont’d …) Logic You have $1 now. How many Euros can you convert this into in 1 year? The current exchange rate is 1.6 $/€ and the European interest rate is 5%. Today: $1 = €0.625 1 year: €0.625 x 1.05 = €0.6563 Implication: $1 today is worth 0.6563 pounds in one year. Investment Analysis Example Your firm just signed a contract to deliver 2,000 batteries in each of the next 2 years to a customer in Japan, at a per unit price of ¥800. It also signed a contract to deliver 1,500 batteries in each of the next 2 years to a customer in Britain, at a per unit price of £6.2. Payment is certain and occurs at the end of the year. The British interest rate r£ = 5% and the Japanese interest rate is r¥ = 3.5%. The exchange rates are 118¥/$ and 1.6$/£. What is the value of each contract?