Simple Sugars

1. Use molecular model to build a linear molecule
2. Ask a student to make a circle out of the structure
1. The student should start pulling model apart ( hydrolysis)
2. And then putting the pc back together synthesis
W
TH
F
M
Today take out worksheet
No Plants today
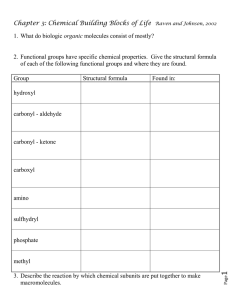
Chemistry Worksheet 1
Chemistry Worksheet 2
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Most organic molecules r 2 big to get into cells
So how do cells get “food”?
Hydrolysis (……………..): process of breaking large organic molecules such as proteins and starches into smaller molecules.
digestion
Large molecules must be hydrolyzed bf they enter a cell
Synthesis : building large organic molecules from small ones
Cells often use food molecules to build larger molecules they need
Carbohydrates
Are sugars
Primary source of Energy, some form structures
3 types
1. Monosaccharides
2. Disaccharides
3. Polysaccharides
How did they get named?
Saccharide = sugar
Monosaccharide disaccharide polysaccharide
Monosaccharides/
Example
• Glucose
Simple Sugars
Were is the most common place to
What life function extracts energy from food?
In what way do glucose and fructose differ?
Both are C
6
H
12
O
6
• Different Simple sugars have different functions because they have different shapes
What do you get when you put two simple sugars together?
Disaccharide’s/
Double sugars
• Made by Putting 2 simple sugars together
• Examples
– Sucrose:
– Lactose:
– Maltose :
Table sugar
Milk sugar
Malt sugar
What do you think many sugars put together are called?
Polysaccharides/ Complex sugars
• They are made from many simple sugars put together
Examples
– Starch: storage in plants
– Glycogen: storage in animals
– Cellulose: Structure- Cell walls in plants
Starch and glycogen are both made from many glucose molecules, so how do the differ?
Polysaccharides/ Complex sugars
• They are made from many simple sugars put together
Examples
– Starch: storage in plants
– Glycogen: storage in animals
– Cellulose: structure in plants
•Different complex sugars have different number and arrangement of simple sugars therefore they have different shapes & functions
Carbohydrates, that need to be stored, are always built into complex sugars. Why would an organism store complex sugars and not simple sugars?
• Cells store excess simple and double sugars by
Complex Sugars sugars are too big to diffuse through biological membranes.
• In order to transport sugars, your digestive system
Simple sugars
1. Is sucrose a simple or double sugar?
2. What class of organic compounds do all sugars belong to?
3. What type of carbohydrate is starch.
4. What kind of organisms make starch?
5. Problem: your blood transports simple sugars, but you eat double and complex sugars. What must your digestive system do to the double and complex sugars?
1. What would your digestive system have to do to a starch molecule bf it could be absorbed by your blood?
2. What would starch be hydrolyzed into?
3. If you have excess glucose in your blood, your liver would build some the glucose into ……………… (poly saccharide)
4. The process of bonding glucose molecules together would be an example of …
5. To what class of organic compounds do sugars belong to?
6. What r the other 3 classes of organic compounds called
Lipids / Fats & Oils
• Many different types
• Are insoluble in water
• Used for
– Energy storage
– Cell membranes
– Steroid hormones
– other
1. What is the scientific name for the group of compounds fats belong to?
2. Structurally lipids vary a lot. So why are molecules that look so different all classified as lipids?
3. Given the following equipment how could you tell a carbohydrate from a fat?
Beakers
Water spoons
Chemical X
Chemical Y
4. Which group of molecules is your bodies primary source of energy?
What is the most diverse class of organic compounds?
Proteins
• Large molecules
• Made up of many different combinations of 20 different types of amino acids
H--C--H
Amino Acid
R can be 1 of 20 different things. So how many different kinds of amino acids are there?
Protein shape, Honors Only
Proteins
• Long folded chains
• Made up of many different combinations of 20 different types of amino acids
• Differences in # and arrangement of amino acids causes proteins to bend into different shapes.
• The shape of the protein determines the proteins function
Function of proteins
1. Defense ex antibodies
2. Structure ex muscle
3. Enzymes ex amylase
4. Transport ex hemoglobin
5. etc
Defence
Structural
Carries Oxygen Enzyme- Regulates chemical reactions
The Order of the Amino Acids
Determines the shape of the protein.
The shape of the protein determines
The Proteins …..!
In general, what is the difference between the protein
Hemoglobin and the protein amylase?
What would happen if your cells put the amino acids in the wrong order when it made a specific protein?
If the order of amino acids in a protein is wrong, usually the protein doesn’t work.
Ex sickled cell anemia is caused 1 incorrect amino acid out of
120 deformed red blood cells
1. Before Proteins can be absorbed from your intestines into your blood, they must be hydrolyzed into ____
2. How many different kinds of amino acids are there?
3. What determines the shape of a protein?
4. What is usually the affect of changing the order of amino acids in a protein
5. The protein you eat is usually not the type of protein your cells need. How do cells get the protein they need?
Nucleic Acids
• Long chains of molecules called
• 2 types
– DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
• Stores hereditary information
– RNA (ribonucleic acid)
• Involved in making proteins nucleotides
1. What smaller molecules are used to build proteins
2. How do you get amino acids? (Trick Question)
3. How many different kinds of amino acids are there?
4. What is the relationship b/n amino acids and the function of a protein?
5. Describe some of the functions of proteins.
6. What happens if your body puts the amino acids in the wrong order?
7. What are the two types of Nucleotides?
8. How do DNA and RNA differ?
1. What is the most abundant inorganic molecule in a living organism? Why is it so important?
2.
Which chemical formula represents an inorganic molecule?
A. C
6
H
12
O
6
B. C
48
H
24
O
6
C. CO
2
D. C
50
H
196
O
73
N
25
S
12
3. Which of the following is a carbohydrate
A. Amylase B. Glycogen C. Glycerol D. Adenine
4. What is the relationship between a simple sugar and a complex sugar?
1. What is the primary function of carbohydrates in organisms
2.
When your digestive system breaks down starch into its components, ______ is formed
3. Which type of carbohydrate could be used by your body the fastest? Explain?
– Sucrose
– glucose
– Starch