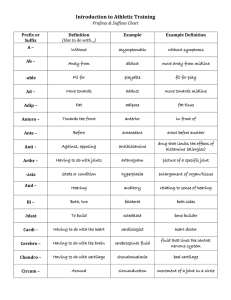
Electrical stimulation Notes What is electricity? A form of that exhibits

Electrical stimulation
Notes
What is electricity?
A form of that exhibits magnetic, chemical, mechanical, and thermal effects; formed from the interaction of positive (+) and negative (−) charges
The physical phenomena associated with the existence and interaction of electrical charge, either static charges (electrostatics) or moving streams of charge (
Types of electricity
Static
Current
)
Static electricity
Static electricity is electricity.
One body gains electrons; the other loses electrons.
Current electricity
A stream of along a conductor
Current types:
Direct current (DC)
Alternating current (AC)
Pulsed current
Direct current
One-directional flow of electrons
Constant and
passing
Alternating current
Bidirectional flow of electrons
No true positive and negative poles
Two terminals of generator (source)
poles
from positive to negative
Pulsed currents
Direct flow of current marked by periods of
Current attributes
Calculated as the
Duty cycle
The of time that the current is flowing relative to the time it is not
ON / (ON + OFF) *100
Example:
20 μsec on, 40 μsec off
20 μsec/ (20 μsec + 40 μsec) * 100
20/60 *100 = 33.3% duty cycle
Pulse width
The length of time a pulse is ON
Measured in micro seconds (μsec)
=
Pulse rate (frequency)
The number of times a
Described as cycles per second
Units of Mega Hertz (MHz)
= millions/second
Current density
The amount of current in the tissues
The higher the current density, the more
Medical devices
Muscle stimulator
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation, NMES
A therapeutic device that delivers current to the body to cause and nerve depolarization
Causes
Nerve stimulator
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator; TENS
Therapeutic device that delivers current to the
body to cause nerve depolarization
Stimulate sensory nerves to
Muscle contraction may occur, but this is not the
purpose of TENS.
What’s the purpose?
Effects
and , which result from the stimulation of sensory and motor nerves
Nerves are polarized – either positive or negative
The electrical current alters the polarization =
Depolarization causes an action potential
Action potential causes a muscle contraction
Single contraction =
Continuous contraction =
Nerve stimulation
Nerves always depolarize in the same order
Sensory
Motor
Muscle fiber
Based on the diameter of the nerve
= depolarize first
Based on location of the nerve
= depolarize first
By stimulating sensory nerves first, the
By stimulating motor nerves, a
is diminished
occurs
By stimulating pain nerves, the feeling of pain is
Electrical stimulation
Notes
Indications
Acute injuries causing pain or edema
Muscle re-education after injury
Contraindications
Areas of (sensory nerve fiber excitement)
Cardiac disability – pacemaker, etc.
Pregnancy
Over the lumbar spine (
Cancerous lesions/tumors
Sites of infection
Exposed metal implants
Treatment parameters & protocols
Electrodes
Completes the circuit between the generator and body
Materials
Metallic (uses sponges)
Silver
Carbon rubber
Self-adhesive
Shape is
Size and placement are of main concern
Determines the and
Current density
of nerves stimulated
Arrangement is based on
Current density
Proximity to each other
Anatomical location
Moving further apart current density in tissues
The electrical current will take the
– not the shortest path possible
Intensity
Increasing intensity causes the current to reach
into the tissue
Usually use an intensity level that is
Duration
Increasing treatment duration the number of nerves stimulated
Depolarization & action potentials
Typical treatment duration is
– ice pack, hot pack, etc.
)
Pre-modulated current
of current with electrodes placed near the site of treatment
Direction of flow is to muscle fibers
– not perpendicular
Machine determines pulse width, duration, frequency
Interferential current
Two channels of different frequencies at the site of treatment
Allows for increased due to
increased amplitude
of equal size
Pair from each of two channels
Crisscross the target tissue
Machine determines pulse width, duration, frequencies
Russian current
Used to
A
after injury
is forced by electrically stimulating the muscle
Patient feels muscle contract, sees muscle contract, and duplicates the response
Intensity is set at while generating a muscle contraction
Pulse width & frequency are set to a duration
needed for
Hold each pulse for minute off
Total treatment time of 15-20 minutes
, with 1