Supplementary methods
advertisement

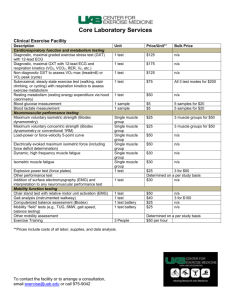
Supplementary methods Twelve plantaris muscles from 10 bullfrogs (Lithobates catesbeianus) were used (Supplementary table 1). Individuals were housed in small groups in vivaria with wet and dry regions, and fed crickets biweekly. Room temperature was maintained at 20 °C. All animal housing and procedures were approved by the UC Irvine Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Frogs were killed by double pithing, the skin stripped from the hindlimbs, and the legs removed at the hip. The plantaris longus muscles and the sciatic nerves were carefully dissected out in oxygenated anuran Ringer’s solution (concentrations in g l-1, 6.78 NaCl, 0.09 KCl, 0.11 CaCl2, 0.23 NaHCO3, 2.0 dextrose; pH7.4) leaving the origin of the muscle connected to the knee joint and the distal tendon largely intact. Sonomicrometry transducers (1 mm diameter; Sonometrics Inc., London, Ontario, Canada) were implanted along a fascicle and secured using 5-0 silk. The knee was clamped to a stereotaxic frame and the distal tendon was secured as close to the end of the muscle as possible in a custom built clamp. The distal clamp was connected to the lever arm of an ergometer (310 B-LR, Aurora Scientific Inc., Ontario, Canada) using steel cable (10 cm). Care was taken to minimize the compliance of the setup. A nerve cuff containing stimulus and ground silver wire electrodes was placed around the sciatic nerve. The preparation was immersed in oxygenated Ringer’s solution at room temperature. Single or trains of square wave stimuli were delivered to the nerve (Grass S48 stimulator, Grass medical instruments, Quincy, MA, USA) and force, muscle length and fibre length logged simultaneously at 5000 Hz (National Instruments AD board (NI USB-6212); Igor Pro 6.31, Wavemetrics Inc., Lake Oswego, OR, USA). In all contractions, muscle length was held constant; however, fibres shortened as series elastic elements stretched during force production. Muscle performance was monitored throughout the experiment by performing regular supra-maximal tetanic contractions. The experiment was terminated once force fell below 80 % of its original value. Peak isometric stress was calculated as peak isometric force in the TetMax condition divided by muscle cross sectional area and corrected for pennation angle (Supplementary table 1). Supplemental Table 1. The basic morphological and physiological properties of the animals and muscle used Frog mass (g) 96.4±7.5 (n=10) Muscle mass (g) 1.5±0.13 (n=12) Resting muscle length (mm) 37.0±0.96 (n=12) Resting fibre length (mm) 14.5±1.08 (n=12) Peak isometric stress (N cm-1) 20.7±2.0 (n=12) Supplemental Table 1. Stimulation parameters for the various stimulation conditions Tetmax Tetsub Twitch Pulse duration (ms) Train duration (ms) Pulse frequency (Hz) Pulse amplitude (V) 0.2 400 100 3-5 0.2 400 100 0.3-0.9 0.2 N/A N/A 3-5