BookKeeping Rule, Accounting Cycle Framework and Record
advertisement

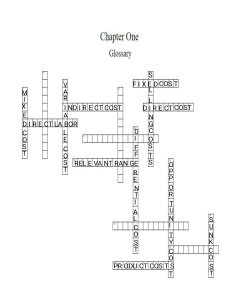
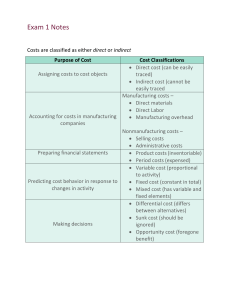
Chapter 15 Accounting for Costs 3/23/2016 1 Accounting for Costs • Cost = a measurement, in monetary terms, of amount of resources used for some purpose. • Variable cost is a cost that varies in total in direct proportion to changes in activity. • Fixed cost is a cost that remains constant in total within the wide range of activity. • Mixed cost is a cost that has both variable and fixed components. cost/volume Average costs = total cost/volume. Average cost behaves differently than total cost. As volume goes up Total fixed cost remains constant, total variable costs goes up, per unit variable costs stays the same, per unit fixed cost goes down, per unit total cost goes down. As volume increases without limit, unit cost approaches variable unit cost and fixed cost per unit approaches zero. Fixed and Variable Costs Fixed costs Non-variable costs = items of cost that, in total, do not vary with volume. • e.g. Building rent, property taxes, management salaries. • Fixed costs are fixed for a range of activity and a limited period of time. • Fixed costs may change for reasons such as a deliberate management decision to change them. Variable costs Items of cost that vary, in total, directly and proportionately with volume. Volume refers to activity level. e.g. Material costs varies with units sold. Electricity costs varies with production hours. Stationery and postage costs varies with number of letters written. Direct and Indirect Costs Direct costs Indirect costs • Costs that can be easily and conveniently traced to a unit of product or other cost object. • Costs that cannot be easily and conveniently traced to a unit of product or other cost object. • Examples: direct material and direct labor • E.g. Wood to make furniture, hours worked on project, flour to make cake. • Example: manufacturing overhead • E.g. rent of a factory that make cars/furniture, manager’s salary. Terms direct and indirect are only meaningful in context of a specific cost object. Can we control costs? • Item of cost assigned to a specific responsibility center that is significantly influenced by actions of manager. • Direct Costs may be controllable (e.g. supplies usage) or non-controllable (e.g. depreciation on equipment or buildings purchased in previous periods). • all indirect costs are non-controllable. Manufacturing Costs (Product cost) Direct Materials Direct Labor The Product Manufacturing Overhead Non-manufacturing Costs (Period cost) Marketing or Selling Cost Administrative Cost Costs necessary to get the order and deliver the product. All executive, organizational, and clerical costs. Activity-Based Costing Direct Cost : Materials & labor Indirect Cost: Overhead Costs First-Stage Allocation Order Size Customer Orders Product Design Customer Relations Other Second-Stage Allocations $/MH $/Order $/Design $/Customer Cost Objects: Products, Customer Orders, Customers Unallocated