Managerial Accounting and Cost
Concepts
Chapter 2
PowerPoint Authors:
Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA
Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA
Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA
Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
2-2
Summary of the Types of Cost
Classifications
Financial
Reporting
Predicting Cost
Behavior
Assigning Costs
to Cost Objects
Making Business
Decisions
2-3
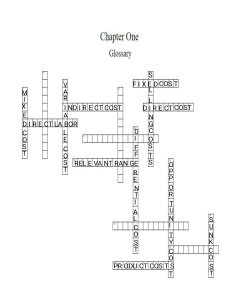
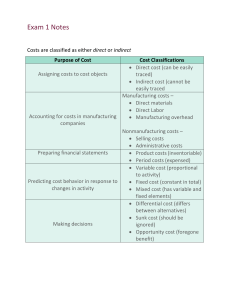
Assigning Costs to Cost Objects
Direct costs
Indirect costs
• Costs that can be
easily and conveniently
traced to a unit of product
or other cost object.
• Costs that cannot be
easily and conveniently
traced to a unit of product
or other cost object.
• Examples: direct
material and direct labor
• Example: manufacturing
overhead
Common costs
Indirect costs incurred to support a number
of cost objects. These costs cannot be
traced to any individual cost object.
2-4
Classifications of Manufacturing Costs
Direct
Materials
Direct
Labor
The Product
Manufacturing
Overhead
2-5
Direct Materials
Raw materials that become an integral
part of the product and that can be
conveniently traced directly to it.
Example: A radio installed in an automobile
2-6
Direct Labor
Those labor costs that can be easily
traced to individual units of product.
Example: Wages paid to automobile assembly workers
2-7
Manufacturing Overhead
Manufacturing costs that cannot be easily
traced directly to specific units produced.
Examples: Indirect materials and indirect labor
Materials used to support
the production process.
Examples: lubricants and
cleaning supplies used in the
automobile assembly plant.
Wages paid to employees
who are not directly
involved in production
work.
Examples: maintenance
workers, janitors, and
security guards.
2-8
Nonmanufacturing Costs
Selling
Costs
Administrative
Costs
Costs necessary to secure the
order and deliver the product.
Selling costs can be either
direct or indirect costs.
All executive, organizational,
and clerical costs.
Administrative costs can be
either direct or indirect costs.
2-9
Cost Classifications for Preparing
Financial Statements
Product costs include
direct materials, direct
labor, and
manufacturing
overhead.
Cost of Good Sold
Inventory
Period costs include all
selling costs and
administrative costs.
Expense
Sale
Balance
Sheet
Income
Statement
Income
Statement
2-10
Prime Costs and Conversion Costs
Manufacturing costs are often
classified as follows:
Direct
Material
Direct
Labor
Prime
Cost
Manufacturing
Overhead
Conversion
Cost
2-11
Variable Cost
Total Texting Bill
A cost that varies, in total, in direct proportion to
changes in the level of activity. Your total texting
bill may be based on how many texts you send.
Number of Texts Sent
2-12
Variable Cost Per Unit
Cost Per Text Sent
However, variable cost per unit is constant. The cost per
text sent may be constant at 5 cents per text message.
Number of Texts Sent
2-13
The Activity Base (Cost Driver)
Machine
hours
Units
produced
A measure of what
causes the
incurrence of a
variable cost
Miles
driven
Labor
hours
2-14
Fixed Cost
Monthly Cell Phone
Contract Fee
A cost that remains constant, in total, regardless of
changes in the level of the activity. Your monthly contract
fee for your cell phone may be fixed for the number of
monthly minutes in your contract.
Number of Minutes Used
Within Monthly Plan
2-15
Fixed Cost Per Unit
Monthly Cell Phone
Contract Fee
However, if expressed on a per unit basis, the average fixed cost per
unit varies inversely with changes in activity. The average fixed cost
per cell phone call made decreases as more calls are made.
Number of Minutes Used
Within Monthly Plan
2-16
Types of Fixed Costs
Committed
Discretionary
Long-term, cannot be
significantly reduced in
the short term.
May be altered in the
short term by current
managerial decisions
Examples
Examples
Depreciation on Buildings
and Equipment and Real
Estate Taxes
Advertising and
Research and
Development
2-17
The Linearity Assumption and the
Relevant Range
Total Cost
Economist’s
Curvilinear Cost
Function
Relevant
Range
A straight line
closely
approximates a
curvilinear
variable cost
line within the
relevant range.
Accountant’s Straight-Line
Approximation (constant
unit variable cost)
Activity
2-18
End of Chapter 2
 0
0