American Free Enterprise: Features & Concepts
advertisement

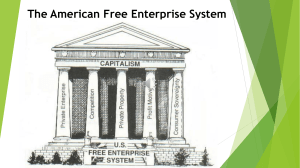
Flow Chart – American Free Enterprise, pgs. 52-53 American Free Enterprise Economic Freedom Property Rights Profit Motive Voluntary Exchange Competition Open Opportunity Definition Definition Definition Definition Definition Definition Benefits Benefits Benefits Benefits Benefits Benefits Chapter 3 – Features of American Free Enterprise Power Point Project, pgs. 51-70 Introduction Slide Include on slide: 1. Title –Features of American Free Enterprise 2. Your Name 3. Picture (Any picture to represent the American Economy) Each additional Slide should have: 1. Title (Feature) 2. Summary and description of the feature 3. Picture(s) to represent each of the features of American Free Enterprise 4. Description of how each picture represents the feature 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Slide 1 – Introduction Slide Slide 2 - Property Rights Slide 3 - Profit Motive Slide 4 - Voluntary Exchange Slide 5 - Competition Slide 6 - Role of the Consumer Slide 7 - Role of the Government (Information and Free Enterprise, Protecting Health, Safety, and Well-Being, Negative Effects of Regulation) Slide 8 - Major Federal Regulatory Agencies (Explain 5 from pg. 55) Slide 9 - Technology and Productivity (include Technological Progress) Slide 10 - Public Good (Include 3 Features, define public and private sector) Slide 11 – Free-Rider Problem and Market Failure Slide 20 – Positive and Negative Externalities Journal Entry: Antz Briefly describe some ways that the movie Antz movie modeled the Command Economic philosophies. Can the ant colony mentality work as an economic system? Explain why or why not. Do you feel that people in the U.S. believe more in the greater good of the “colony”, or the individual? Explain your answer. Chapter 3 – Journal Entry Describe in your own words, why you feel that economic freedom, property rights, profit motive, voluntary exchange and competition are beneficial to the American economy. Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 1. 2. There are over 18 million businesses in the United States; 3 million minority-owned businesses. America has been a place where anyone, from any background can achieve success. Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 3. Describe the following goals of the U.S. Government: 1. Employment – provide jobs for everyone who is able to work (economists consider 4-6% desirable; current 9.7) 2. Growth – each generation should enjoy a higher standard of living; economy must provide additional goods and services each year (GDP 3. Stability – keeping economy stable and secure gives consumers, producers, and investors confidence 1. Price – gov’t aims to prevent sudden, drastic shifts in prices; prices up – hurts consumer, prices down – hurts producers 2. Financial Institutions – banks are secure, money protected from fraud or mismanagement Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 5. 6. Features of Public Goods: 1. Consumers pay individually: is impractical. Government collects taxes to fund programs. 2. Excluding nonpayers: certain facilities should be available to all, excluding nonpayers is unrealistic. 3. Any number of consumers can use them without reducing the benefits to any single consumer. Military, interstate highway, waste management, national parks, firefighter, education Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 7. 8. 9. 10. Cost and Benefits 1. The benefit to each individual is less than the cost that each would have to pay if it were provided privately 2. The total benefits to society are greater than the total cost Public sector finances and produces public goods, private sector involves transactions of individuals and businesses. Free Riders are people who do not pay for certain goods or services, but reap the benefits of it. Market Failures are situations when the market, on its own, does not distribute resources efficiently. • Certain production is impractical and does not generate profit, such as roads, highways. • Education, paid for through taxes. Certain people do not pay taxes, yet reap the benefit of education. Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 11. 12. 13. Externality – an economic side effect/impact of one person’s actions, that generates benefits or costs to someone (bystander) other than the person deciding how much to produce or consume Positive externality – beneficial side effects of the production of goods and services • Education creates a positive externality because the more educated people are less likely to engage in violent crime, which makes everyone in the community, even people who are not well educated, better off. Negative externality – negative side effect of the production of goods and services • Theft and losses endured by WalMart, are passed on to the consumers by way of increased prices on goods Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 14. Goals of the Government: 1. Encourages the creation of positive externalities, such as education 2. Aims to limit negative externalities, such as acid rain created from power plants and auto emissions Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 15. 16. 17. Poverty threshold is an income level below that which is needed to support families or households. Poverty threshold in the United States in 2002: • Single parent under age 65, with one child, $12,120 • Four person family with two children, $18,400 Established in the 1930s, the government welfare plan collects taxes from individuals, then redistributes them to others. Government aid for the poor. Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 15. 16. Cash transfers are direct payments of money to poor, disabled, and retired people. Cash Transfers 1. Temporary Assistance for Needy Families – TANF replaced the AFDC discontinued direct federal welfare; sends money to states, which design and run their programs. States must adhere to strict federal rules; designed to free people from welfare dependence 2. Social Security – created in 1935, during the great depression, provides cash transfers of retirement income to the elderly and living expenses to disabled Americans. Takes payroll taxes from current workers and redistributes them to current recipients 3. Unemployment Insurance – Funded by federal and state governments. Unemployment checks provide money to eligible workers who have lost their jobs through no fault of their own 4. Workers Compensation – state funded program that pays injured workers money for the lost wages they have endured as a result of their injuries Chapter 3 – American Free Enterprise 20. 21. 22. 23. In-kind benefits are goods and services that are provided for free or at greatly reduced prices. • Food stamps, subsidized housing, legal aids, etc. Medical benefits provided in the united states are based on categories such as health insurance for the elderly, disabled, and poor • Medicare covers Americans over 65, as well as the disabled • Medicaid covers poor who are unemployed or not covered by employers insurance plans Federal, state, and local governments all provide educational opportunities. Education programs add to a nation’s human capital and labor productivity. President Bush challenged “faith-based initiatives” (charities, community groups, churches) to assist people in need. Traditionally, shown the ability to save and change lives. Due Friday 9 - 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Antz Video Questions Flow Chart– Free Enterprise Chapter 3 Guided Reading Worksheet Crossword Puzzle VIS Terms Chapter 3 – VIS Terms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Property Rights Profit Motive Voluntary Exchange Consumer Sovereignty Public Goods Public Sector Private Sector Free Rider Externalities Welfare