Free Enterprise Notes
advertisement

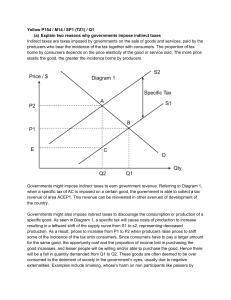
Chapter 3 American Free Enterprise Features of American Free Enterprise Economic Freedom Competition Private Property Self-Interest Contracts Voluntary Exchange Profit Motive Economic Freedom Individuals – work wherever they choose Businesses – hire whomever they choose Government – minimal intervention Competition Producers have an incentive to ‘beat the competition’ Consumers benefit as a result Think of one way that each fast food provider has tried to beat the competition? Why are the Buffalo almost extinct and Cows are not? Private Property Individuals and businesses can buy and sell property and limit its use. Contracts Individuals and Businesses form written agreements that are legally binding. Self-Interest Consumers and businesses operate to their own benefit. Their decisions do not have to please the government, other consumers, or other producers. Voluntary Exchange Both consumers and producers gain from voluntary exchange of goods/services. Profit Motive Profit is a powerful incentive that leads entrepreneurs to accept the risk of failure. Explain what this quote means “Taxes are what we pay for civilized society” Oliver W endell Holmes Jr., 1904 What services does the Government provide to the American People? Public Works Medicaid/Medicare Disaster Relief Unemployment Welfare Police, Fire Education Roads Social Security Public Transportation Grants Why does the Government Produce Goods and Services? Public goods: a good/service that can be used by many at the same time without diminishing any one person’s consumption; it is difficult to exclude someone from the good. Examples The "free-rider" problem Why don’t towns charge admission for 4th of July fireworks displays? Why does the Government Produce Goods and Services? Externalities are defined as third party (or spill-over) effects arising from the production and/or consumption of goods and services for which no appropriate compensation is paid. Examples of positive externalities a beautiful garden on a busy street the safer neighborhood for others that results from some residents hiring private security patrols What is significant about this picture? What does it tell you about private property? Free-Rider Someone who would not pay for a service, but would get the benefits if it were a public good. Why is there pollution? Examples of negative externalities include an unmowed lawn in a suburban neighborhood, or automobile exhaust, or second-hand cigarette smoke. Externalities What are the externalities created? Snowplowing A poker room Garbage Pickup Homelessness Broken Windows Theory "One unrepaired broken window is a signal that no one cares, and so breaking more windows costs nothing." Broken windows policing assumes that serious crime can be reduced by strongly enforcing minor crimes. The "broken window" theory suggests that neighborhood order strategies such as those listed below help to deter and reduce crime. Quick replacement of broken windows Prompt removal of abandoned vehicles Fast clean up of illegally dumped items, litter and spilled garbage Quick paint out of graffiti Finding (or building) better places for teens to gather than street corners Fresh paint on buildings Clean sidewalks and street gutters Why does poverty exist in the United States? What Safety nets exist? Public Goods that cannot be privately provided Why does the Government Produce Goods and Services? Merit goods: goods/services that have a social value over and above their utility for the individual consumer. What are the benefits of having a good school in your community? Examples of Merit Goods IS THIS AN EXAMPLE OF MERIT GOOD? WHY OR WHY NOT?