Standard 7-4: The students will demonstrate an understanding of the
advertisement

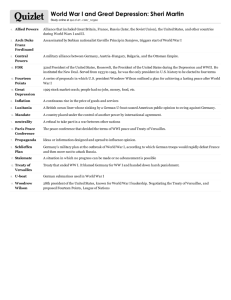
Standard 7-4: The students will demonstrate an understanding of the causes and effects of world conflicts in the first half of the twentieth century. Enduring Understanding The influence of both world wars and the worldwide Great Depression are still evident. To understand the effects these events on the modern world, the student will utilize the knowledge and skills set forth in the following indicators: Indicators 7-4.1 Explain the causes and course of World War I, including militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism, the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the impact of Russia’s withdrawal from, and the United States’ entry into the war. What were the MAIN causes of World War I? militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism How did militarism lead to World War I? European nations continued to build up their armies and navies not only for defense but also to conquer other lands. How did alliances lead to World War I? There were rivalries among the European nations and this led many to join in secret alliances with other countries. Russia, France, and Great Britain formed an alliance and Germany, Italy, and Austria-Hungary formed an alliance. How did imperialism lead to World War I? Imperialism fueled the competition among European countries. How did nationalism lead to World War I? Not only did some European groups want independence from empires, but nationalism spurred economic and political rivalries. How did World War I start? A Serbian nationalist killed Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir to the Austro-Hungarian Empire which prompted Austria-Hungary to declare war against Serbia. Quickly, nations honored their alliances and most of Europe was at war. Why was World War I so deadly? New weapons such as long range artillery, poison gasses, submarines, tanks, machine guns, airplanes, and flame throwers, as well as trench warfare Who fought in the Western Front? Germany fought against French and British troops. Fighting here continued throughout the war. Neither side was able to get victory. Who fought in the Eastern Front? Germany and Russia mainly fought on this front. When Russia withdrew, Germany was able to move troops to the Western Front. Who fought in the Italian Front? Italy and France fought against the German and Austro-Hungarian troops. Why did Russia drop out of the war? The Russian Czar was overthrown in the Bolshevik Revolution. Lenin took power and signed a treaty with Germany, leaving the British and French forces to continue the war. Why did the U.S. enter the war? German submarines sunk the British Lusitania with Americans on board; the British intercepted and published the Zimmerman Telegram to Mexico (promising U.S. land if Mexico joined Germany); Germany began sinking U.S. merchant ships. When was the armistice that ended the fighting in World War I? November 11, 1918 7-4.2 Explain the outcome and effects of World War I, including the creation of Wilson’s Fourteen Points, the Treaty of Versailles, shifts in national borders and the League of Nations. What peace treaty was constructed by the Allies after World War I? Treaty of Versailles What was the main focus of the European leaders in constructing the Treaty? They wanted to punish Germany. What was the main focus of President Wilson in constructing the Treaty? He wanted to focus on the M.A.I.N. causes of World War I such as no military build-up, no secret alliances, and the right to self determination (right to choose one’s own government). What was Wilson’s Fourteen Point Proposal? Wilson presented his ideas for peace in this proposal. The fourteenth point was the creation of the League of Nations. What were the main features of the Treaty of Versailles that weakened Germany? 1. Germany had to accept responsibility for starting the war (War Guilt Clause). 2. Germany had to pay reparations to the Allies for the cost of war. 3. Germany’s military was restricted to 100,000 soldiers, no air force or submarines. 4. Demilitarization of the Rhineland. 5. Loss of all imperial possessions. What were the weaknesses of the League of Nations which was established by the Treaty of Versailles? 1. Not all major powers including the U.S. were members. 2. Germany and Russia were not allowed to join at first. 3. Japan and Italy withdrew. 4. The League had no authority or army to enforce decisions. 5. All decisions had to be unanimous. What countries were formed with the breakup of the Austro-Hungarian Empire? Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Austria, and Yugoslavia What countries were formed with the breakup of the Ottoman Empire? Turkey, and mandates in the Middle East What countries were formed from Russia? The Soviet Union, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland 7-4.3 Explain the causes and effects of the worldwide depression that took place in the 1930s, including the effects of the economic crash of 1929. What factors caused economic problems in Europe? War time spending, rebuilding costs, and widespread unemployment with the return of troops What hurt the U.S. stock market? Europeans quit buying because of their own economies; Americans bought stocks on margin; there was a surplus of goods in America. What was the stock market crash? Prices were inflated and investors stopped buying in order to pay back loans. The prices of stocks dropped. What was the Great Depression? Factories shut down or laid off workers, causing high unemployment. Banks called in loans and if people couldn’t pay, their houses and farms were taken. How did the effects of the Depression in the U.S. affect European countries? The U.S. stopped loaning money to European countries and began calling in the loans they had already made to them. How did most nations respond to the Depression? They followed a policy of isolationism in an effort to solve their economic problems. How did most democratic nations try to solve their economic problems? They passed laws to help their people such as the New Deal in America. How did totalitarian nations try to solve their economic problems? They turned to imperialism to gain raw materials and markets to stimulate the economy. What was the New Deal? This was a series of programs designed to provide relief to the people and regulate the stock market, banks, and production. This greatly increased the national government’s role in the economy and lives of the American people. How did Great Britain respond to the Depression? Great Britain raised tariffs to protect their businesses and raised taxes to back loans to businesses. How did Germany react to the Depression? Germany printed more and more money until it was worthless. Hitler, Mussolini, and military leaders in Japan took advantage of the economic anxiety. 7-4.4 Compare the ideologies of socialism, communism, fascism, and Nazism and their influence on the rise of totalitarian governments after World War I in Italy, Germany, Japan, and the Soviet Union as a response to the worldwide depression. What is socialism? Socialism is an economic system where all means of production (factories), land, and property are owned by society as a whole – represented by the government. What is Communism? Communism is a kind of socialism but involves a revolution of the working class and the government oversees the collective ownership of business and property. What changes did Stalin bring to the Soviet Union? He made the country an industrial power, had secret police, censored all sources of information, and used propaganda to keep power. He ordered Five-Year Plans to increase industrialization. He collectivized farms. What is fascism? This is an extreme form of nationalism where the country is put above anything else. People had no freedom. Who was Mussolini? He was the fascist leader of Italy. Who was Hitler? He was the fascist leader of Germany. He helped found the Nazi Party and gained control of the government. He thought the “Aryans” were the “master race” and blamed others, especially the Jews, for Germany’s problems. He ignored the Treaty of Versailles. How did the Depression affect Japan? As a newly industrialized country, Japan was dependent on the world market, so when the market turned, Japan blamed the West (Europe and America). Military leaders thought expansion into the Asian mainland (China and French Indochina) would bring economic prosperity. 7-4.5 Summarize the causes and course of World War II, including drives for empire, appeasement and isolationism, the invasion of Poland, the Battle of Britain, the invasion of the Soviet Union, the “Final Solution,” Lend-Lease, Pearl Harbor, Stalingrad, the campaigns in North Africa and the Mediterranean, the D-Day invasion, the island-hopping campaigns, and the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Why was Italy unhappy with the Treaty of Versailles? Italy fought on the side of the Allies but was not given a large amount of land. Why was Germany unhappy with the Treaty of Versailles? Germany was especially unhappy that they were forced to accept responsibility for the war and pay reparations. How was Italy aggressive prior to World War II? Italy attacked Ethiopia in Africa and Albania. How was Germany aggressive prior to World War II? Hitler began increasing his army; sending troops to the Rhineland; adding Austria; and taking the Sudetenland and then all of Czechoslovakia. What was the response of Great Britain and France during this aggression? They practiced a policy of appeasement. What was agreed at the Munich Conference? France and Britain agreed that Germany could have the Sudetenland if they would stop taking any more land. How was Japan aggressive prior to World War II? Japan invaded Manchuria and then China. How did World War II start? Germany invaded Poland in a blitzkrieg and divided it with the Soviet Union. Then Great Britain and France declared war on Germany. What was the Battle of Britain? After France surrendered, Germany attacked Great Britain with his Air Force. The British were able to decode messages and use radar to stop Germany. What was the Battle of Stalingrad? The Germans attacked the Soviet Union and finally handed the Germans their first defeat. What was the “cash and carry policy”? The U.S. stopped their policies of isolationism and neutrality and began selling war materials to Great Britain if they would pay cash for them and carry them to Britain. What was the Lend-Lease Act? The U.S. would lend or lease weapons and other supplies to countries in support of the allies. Why did Japan attack Pearl Harbor? The U.S. froze Japanese bank accounts and stopped selling oil to Japan. What did the U.S. do after Pearl Harbor? The U.S. declared war on Japan and then Germany and Italy declared war on the U.S. What were the two theaters of World War II? Pacific and European What kind of strategy was used in the Pacific Theater? Island-hopping or leapfrogging How did the Allies stop the Italians? The Allies took back Northern Africa and then went into Italy. What was D-Day? The Allies landed on the beaches of Normandy, France, and began to liberate France from German control. What was the Battle of the Bulge? This was the final German offensive. The Allies were able to force a retreat, causing the German’s to surrender. How did the war in the Pacific Theater end? Finally, President Truman ordered to bombing of Hiroshima and then Nagasaki before the Japanese surrendered unconditionally. 7-4.6 Analyze the Holocaust and its impact on European society and Jewish culture, including Nazi policies to eliminate the Jews and other minorities, the Nuremberg Trials, the United Nations Declaration of Human Rights, the rise of nationalism in Southwest Asia (Middle East), the creation of the state of Israel, and the resultant conflicts in the region. What caused Hitler’s anti-Semitism? Jews were often scapegoats during times of crisis. The Jews were blamed for Germany’s economic trouble. What did the Nazis believe was the “master race”? The Nazis thought Germans were the superior race and used the term “Aryan” to describe them. All others were inferior, including the Jews, Poles, Russians, Gypsies, etc. What were the Nuremberg Laws? These were laws designed to take away the rights of Jews in Germany. What was Kristallnacht? This was the “Night of Broken Glass” and the beginning of the Holocaust. Jewish businesses and synagogues were destroyed. What was the Holocaust? The Holocaust was a time when Jews were forced into ghettos or concentration camps. By the War’s end, six million Jews were killed and perhaps another 5 million non-Jews. What was the “Final Solution”? This was the extermination of all the Jews. How was the nation of Israel created? After the Holocaust, many Jews wanted a homeland (a Zionist state). The U. N. divided Palestine and created Israel. How did Palestine lose their homeland? As soon as Israel was created, Palestine declared war on Israel and eventually lost all their land. How did Egypt get control of the Suez Canal? The Egyptian President Nasser wanted to rid Egypt of foreign influence and take control of the Canal. He fought for it and lost but eventually he did get control of the Canal. What is the Palestinian Liberation Organization? The PLO wants to have a Palestinian state in the areas of Israel where they live— especially in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights? This is a listing of specific rights every individual should have regardless of nationality.