4_P5
advertisement

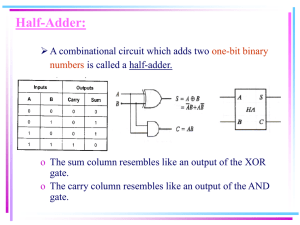
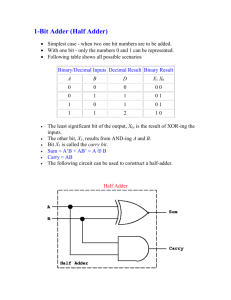
Spezielle Anwendungen des VLSI – Entwurfs Applied VLSI design Course and contest Adder structures Sebastian Kruse Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 1 Types of adders • Redundant • Carry-Save (CSA) • Redundant-Binary (RBA) • Not redundant (CPA) • Ripple-Carry (RCA), Manchester-Carry-Chain (MCC) • Carry-Skip (CSK), Carry-Select (CSEL) • Carry-Lookahead (CLA), Conditional-Sum (CSUM) • Asynchronous adder Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 2 Ripple-Carry adder • • • Serialization of full adders Small area but slow speed In general the best adder for FPGA • FPGA uses LUTs instead of AND, OR, XOR, NOT • Optimized logic which speeds up RCA an-1 bn-1 cout FA sn-1 a1 b1 cn-1 c2 FA s1 a0 b0 c1 FA s0 cin Delay time Area Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 3 Carry-Skip adder • Adder with square timing complexity and low area • Area compared to RCA: 1 𝑋𝑂𝑅/𝑏𝑖𝑡, 1 𝐴𝑁𝐷/𝑔𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑝, 1 𝑀𝑈𝑋/𝑔𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑝 • Idea: parallel calculation CPA CPA 𝑠𝑖−1:𝑘 0 1 CPA 0 1 𝑠𝑛−1:𝑖 Delay time Area Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 4 Carry-Lookahead adder • Fast adder with logarithm complexity but high area • Idea: carry is calculated in advance CLA-Block 𝑐0 = 𝑐0′ 𝑐1 = 𝑔0 ∨ 𝑝0 ∧ 𝑐0′ 𝑐2 = 𝑔1 ∨ 𝑝1 ∧ 𝑐1′ = 𝑔1 ∨ 𝑝1 ∧ 𝑔0 ∨ 𝑝1 ∧ 𝑝0 ∧ 𝑐0′ … 𝑝3′ = 𝑝3 ∧ 𝑝2 ∧ 𝑝1 ∧ 𝑝0 𝑔3′ = 𝑔3 ∨ 𝑝3 ∧ 𝑔2 ∨ 𝑝3 ∧ 𝑝2 ∧ 𝑔1 ∨ 𝑝3 ∧ 𝑝2 ∧ 𝑝1 ∧ 𝑔0 • Types of implementation (for carry generation) • Slansky • Kogge-Stone • Brent-Kung • Han-Carlson Delay time Area Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 5 Brent-Kung • Idea: use binary tree for carry propagation (𝑔0 , 𝑝0 ) 𝑐0 (𝑔1 , 𝑝1 ) carry tree 𝑐1 (𝑔2 , 𝑝2 ) (𝑔3 , 𝑝3 ) inverse carry tree • Two tree structures 𝑐2 𝑐4 𝑐3 𝑐5 (𝑔4 , 𝑝4 ) (𝑔5 , 𝑝5 ) 𝑐6 (𝑔6 , 𝑝6 ) (𝑔7 , 𝑝7 ) 𝑐7 • Carry collection • Carry redistribution Delay time Area Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 6 Comparison on FPGA • RCA • • Area : 103 Max. frequency : 431,779 MHz • CSK • • Area : 125 Max. frequency : 384,025 MHz • Brent Kung • • Area : 109 Max. frequency : 409,500 MHz Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 7 Comparison on ASIC • RCA • • • • Core size : 4634,45 µm² Max. frequency : 3180 MHz Pdyn : 22,154 mW Pleak : 9,875 µW • CSK • • • • Core size: 4324,63 µm² Max. frequency : 2910MHz Pdyn : 18,651 mW Pleak : 8,346 µW • Brent Kung • • • • Core size : 4392,61 µm² Max. frequency : 2980 MHz Pdyn : 19,406 mW Pleak : 8,716 µW Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 8 Thank you for your attention! Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 9 Half / full adder • Half adder ((2,2)-counter) a b cout 𝑠 =𝑎𝑏 𝐶𝑜𝑢𝑡 = 𝑎 ∧ 𝑏 HA s • Full adder ((3,2)-counter) a b cout FA cin 𝑠 = 𝑎 𝑏 𝑐𝑖𝑛 𝐶𝑜𝑢𝑡 = (𝑎 ∧ 𝑏) ∨ (𝑏 ∧ 𝑐𝑖𝑛 ) ∨ (𝑎 ∧ 𝑐𝑖𝑛 ) s Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 10 Comparison of adders CSK 60 tp(nsec) Brent-Kung RCA 40 Brent-Kung 20 0 0 10 Area (mm2) 80 0.4 RCA CSK 0.2 0 20 0 10 20 Number of bits Number of bits Source: mountains.ece.umn.edu (2006) Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 11 Kogge-Stone Institute of Applied Microelectronics and Computer Engineering College of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock Slide 12