Nutrition
advertisement

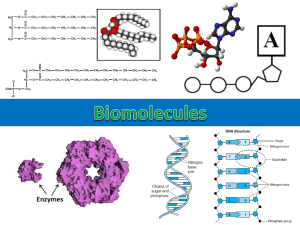
Nutrition • Why do we need food? • Energy • Provides raw materials for growth and repair • Makes chemicals needed for metabolic reactions • The 6 most common elements in food are: • • • • • • Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) Nitrogen (N) Phosphorous (P) Sulphur (S) Other elements occur in smaller numbers: 5 as dissolved salts • Sodium (Na) • Magnesium (Mg) • Chlorine (Cl) • Potassium (K) • Calcium (Ca) 3 as trace elements (only needed in tiny amounts): • Iron (Fe) • Copper (Cu) • Zinc (Zn) • The 6 groups of Biomolecules are: • • • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids (Fats and Oils) Proteins Vitamins Minerals Water Carbohydrates Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) & Oxygen (O) • In the form of Cx (H2O)y • Made of sugar units: –Monosaccharides –Disaccharides –Polysaccharides Monosaccharides • Smallest unit of carbohydrate • Sweet • Soluble in water • Glucose • Fructose Disaccharides • Two monosaccharides joined together • Sweet • Soluble in water • Sucrose (table sugar)=glucose + fructose • Maltose=glucose +glucose Polysaccharide • Many monosaccharides joined together • Insoluble in water • Starch • Cellulose • Glycogen Functions of Carbohydrates • Provides energy (Metabolic Role) • However if too many carbohydrates are consumed it will be converted to fat and stored • Cellulose in plant cell walls (Structural Role) • Cellulose also has the function of preventing: – Constipation – High Blood Cholesterol Lipids(Fats and Oils) Carbon (C), Hydrogen(H) and Oxygen(O) • Less oxygen than Carbohydrates • Fats are solid at room temp, oils are liquid • Lipid structure varies; – Triglyceride(normal lipid): one glycerol with 3 fatty acids joined to it – Phosopholipid: one glycerol, 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group joined to it Triglyceride Functions of Lipids • Lipids release energy in respiration (Metabolic role) • They also form a protective layer around delicate organs such as the heart (Structural role) • They act as an insulator, stored as adipose tissue under the skin • Lipids are insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol • Sources of lipids include butter and cod liver oil. Proteins Carbon(C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) • Made of amino acids joined together in different ways • 26 amino acids in total • Dipeptide is a chain of 2 amino acids (think 2 marbles joined) • Tripeptide is a chain of 3 amino acids • Peptide is a chain of less than 20 amino acids • Polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids (apx 500) • There are essential amino acids which cannot be made by animals and must be consumed in the diet (9 in total) • Fibrous Protein: have very few or no foldings e.g. keratin in hair and nails • Globular Protein: have lots of foldings e.g. Enzymes • Prions are proteins that do not fold incorrectly • Eg: Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease and BSE Protein Functions • Form enzymes and hormones (Metabolic Role) • Present in hair, nails and muscle (Structural Role) Sources: Meat, Fish, Eggs and Nuts Vitamins • Most Vitamins cannot be made by the body • Only needed in small amounts • Water Soluble Vitamins: B group and C • Fat Soluble Vitamins: A/D/E/K Vitamin C • Found in Oranges, forms connective tissue. • Deficiency Scurvy: Bleeding gums, loose teeth Scurvy Vitamin D • Found in Cod liver, for healthy bones. • Deficiency Rickets. Minerals • Necessary in small amounts • Form structures e.g. Calcium forms bones and cell walls • Forms soft body tissue e.g. Muscles • Maintains concentration of cells and body fluids • Minerals needed by plants and animals vary. • Animals: • Calcium, found cheese, forms bones and teeth • Iron, found in liver and green vegetables, forms part of haemoglobin • Plants: • Calcium, absorbed from soil, forms calcium pectate in cell walls • Magnesium, absorbed from soil, is part of the structure of chlorophyll Water • Water makes up the major body cells and helps them to keep their shape • It helps transport materials in and out of cells • It is a good solvent • Necessary for photosynthesis Nutrient Function Source Carbohydrates •Sugars •Starch •Fibre Energy Energy Prevents constipation Sweets, fizzy drinks Bread, potatoes, rice Brown bread, fruit Fats Energy Insulation Butter, oil, cream Proteins Growth and repair Meat, fish, eggs, nuts Vitamins •Vitamin C Healthy skin and gums Oranges •Vitamin D Strong bones Dairy products Minerals •Iron Haemoglobin which Red meat, egg yolks carries oxygen in blood •Calcium Strong bones Milk, cheese Water Allows cells to work Drinks, vegetables 2010 Section A Q1 Higher