IC and CZE Lab
advertisement

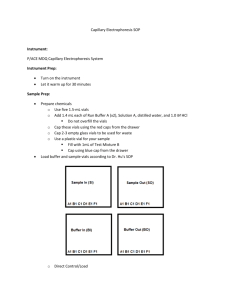
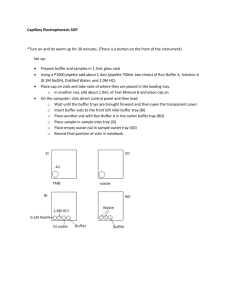
Brittany Hicks IC & CZE Lab- Dr. Foy Spring 2013 Ion Chromatography and Capillary Electrophoresis Introduction Ion chromatography is a specific type of liquid chromatography. The main purpose of this chromatography is to analyze aqueous solutions for specific ion levels. Using a column, the IC separates different anions. As seen before in our liquid chromatography lab, the IC uses a liquid mobile phase and also a stationary phase which is either liquid or a solid. The plate height should be minimized and number of theoretical plates maximized under analysis for best results. Capillary Electrophoresis is able to separate ions because of their mobility within an electric field. Charge to mass rations and the attraction to additives in the background both help in aiding in determining the mobility of a specific substance. The most commonly used samples within the CZE are proteins and enzymes. Procedure – IC Before operating the instrument, check the helium tank in the gas room o If tank pressure is below 80 psi, let lab assistants and/or instructor know If pressure is below 40 psi, the tank must be replaced Turn the helium gas on using the knob behind the instrument o The pressure gauge should read 9 psi If the pressure is not near 9 psi, turn the black knob in front of the gauge in the direction the needle needs to move Check the Regenerant and Eluent bottles on the instrument o If either bottle is less than half full, refill using containers near the instrument or make more (regenerant should be replaced weekly) To make more eluent, use 10mL concentrated eluent and dilute to 1L with distilled water To make more regenerant, use 5mL 6M sulfuric acid and dilute to 2L with distilled water Open the Chromeleon program from the icon on the desktop Equilibrate the instrument o In Chromeleon, choose File>Open o Change the file type to Control Panel and the folder to MyPanels o Open ICS-90 System o Turn the pump off in the program o Turn the small black knob on the pump to the left (one turn only) Do not touch the knob that says DO NOT TOUCH Let the system purge for 30 seconds Make sure that eluent is flowing into the waste jug below the counter o Turn the pump on in the program, but leave the knob alone Let the system purge for another 30-45 seconds Make sure that eluent is dripping into the waste jug below the counter o Turn the knob on the pump back to the right, but do not over-tighten o Let the system equilibrate for 20-30 minutes o Check the flow of the eluent by using a graduated cylinder to collect the waste There should be graduated cylinders below the counter with the waste jugs If the instrument is equilibrated, the flow should be ~1mL/1min If the flow is less than ~1mL/min, wait another 10-15 min and check again If there is less than ~1mL/min, and the instrument has been equilibrating for 40-60 min, find the experts, lab assistants, or Dr. Foy Setting up the software o Create a new sequence by clicking File>New>Sequence (From Wizard) o Once the wizard opens, click Next twice o Under the Specify Unknowns screen, adjust the number of vials (if you are not running unknowns, this number is zero), the title format of the unknowns (i.e. Campbell Hall Water), the number of injections per vial (typically one), the start position (if you are running one standard, the unknown’s position would be 2), and injection volume (should always be 10 μL) o Click Apply, then Next o Under the Specify Standards screen, adjust the number of vials (should always be running one 7-anion standard), the title format (i.e. Seven Anion Standard), the number of injections per vial (typically one), the start position (should always be 1), and injection volume (should always be 10 μL) o Click Apply, then Next o Under the Methods and Reporting screen, change nothing and click Next o Under the Saving the Sequence screen, choose a name for your sequence and a title for it (top two boxes; ensure that these have your initials), but leave the bottom two boxes unchanged) o Click Finish o The sequence should now be in your window Running the Sequence o Click Batch>Edit>Add Sequence and choose your sequence o Click Start o The software will prompt you to inject your first standard o Fill a sterilized syringe halfway with your standard, then press it onto the injector (ensure that it is fully on the injector) o o o Slowly inject the sample until you see 4-5 drops come out into the waste beaker Click OK in Chromeleon This scan should take 16 minutes If it does not, consult the experts, lab assistants, or Dr. Foy If there are no peaks after 16 minutes, your sample was not injected properly If there are no peaks after several injections and/or the conductivity is very high, replace the regenerant Naming Peaks o Open your sequence File>Open File type should be Sequence Select your sequence o Double click 7-anion standard in the dialogue box that lists the names of your injections o Find the Peak Analysis tab o Double click the first positive peak o A dialogue box will appear Name each peak according to the sheet in the drawer which shows a spectrum of the standard, then press Enter There is no peak for the acetate ion Shutting Down o In the Batch menu, select Stop o Leave Chromeleon running (the system will go into low flow after 6 hours of inactivity) o Fill the eluent to the top o If the waste container is full, move the tube into a new container and do the following: Put a cap on the full waste container Bring the full container to the prep room using the elevator Neutralize the waste in a large beaker on a stir plate with magnetic stir bar using 20 mule team borax (located in storage area, consult lab assistants or Mrs. Mowery if you need help) Use universal indicator to check the pH (the color should change from pink to green) Flush the waste down the drain with plenty of water o Be sure to turn off the helium knob behind the instrument Lab Procedure: Run four different water samples o Do not run salt water or flavored water as this will harm the instrument! Run two samples per day Run two trials of each sample Follow the Standard Operating Procedure o Day 1: o Unknown samples should be 2 vials and 2 injections per vial The first injection is the standard, followed by 2 injections of each sample Be sure to use the same standard for both days Day 2: Same procedure as Day 1 Make a calibration curve of your samples Plot ppm vs. height and area Ask experts, assistants, or Dr. Foy if you have any questions Procedure – CZE Chemicals Required: Capillary Performance Test Mixture B (mixture of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and phydroxyphenylacetic acid) Capillary Performance Run Buffer A (pH 8.35) Capillary Electrophoresis System Solution A (0.1 M NaOH) Distilled water 1.0 M HCl Solution All chemicals should be stored in the chemical refrigerator or under the instrument Standard Operating Procedure: Turn on the instrument Let it warm up for 30 minutes Read the Dr. Hu’s SOP while the instrument is warming up Prepare chemicals o Use five 1.5-mL vials o Add 1.4 mL each of Run Buffer A (x2), Solution A, distilled water, and 1.0 M HCl Use P1000 micropipette and dispense two quantities of 700 μL for each solution o Do not overfill the vials o Cap these vials using the red caps from the drawer o Cap 2-3 empty glass vials to be used for waste o Use a plastic vial for your sample Fill with ~1mL of Test Mixture B Cap using blue cap from the drawer Load buffer and sample vials according to Dr. Hu’s SOP o Direct Control>Load Wait until buffer trays are sent to the front, lift the cover, and insert vials as follows: BI:A1 – 0.1 M NaOH BI:B1 – 1 M HCl BI:C1 – distilled water BI: D1 – Buffer A BO:A1 – Waste BO:B1 – Waste BO:C1 – Buffer A SI:A1 – Test Mix B SO:A1 – Waste Record the position of each vial in your lab notebook Build Method o Use Dr. Hu’s SOP for more details on how to build method o Initial Condition: Leave all defaults o PDA Detector Initial Conditions: Use Channel 1 (check both boxes) at 214 nm, uncheck Acquisition Enabled (top left quadrant) o Time Program: Rinse 1.0 min (20 psi, forward pressure) from 1.0 M HCl to Waste Rinse 1.0 min (20 psi, forward pressure) from distilled water to Waste Rinse 2.0 min (20 psi, forward pressure) from 0.1 M NaOH to Waste Rinse 1.0 min (20 psi, forward pressure) from distilled water to Waste Rinse 2.0 min (20 psi, forward pressure) from Buffer A to Waste Inject (0.5 psi pressure, 10 seconds) from sample vial (Test Mixture B) to Waste Separate at 0.0 min (Duration: 7 min, Voltage: 25 KV, Ramp: 0.17 min) from Run Buffer A (BI) to Run Buffer A (BO) Autozero at time 1.50 min Stop data at 7.0 min Rinse 1.0 min at time 8.0 min (20 psi, forward pressure) from distilled water to Waste o Be sure to use the SO waste for the injection and be sure to use both of the BO waste vials throughout the time program Save and Run Method o Use Dr. Hu’s SOP for more details on how to do this Save and print electropherogram with report o PRINTER MAY BE DOWN! SEE EXPERTS, LAB ASSISTANTS, OR DR. FOY If you are the last group, exit the program, remove your vials and turn off the instrument o FOR INSTRUMENT SHUT DOWN: Be sure to leave a buffer vial in the buffer inlet and buffer outlet trays Choose to inject the tray Allow the tray to inject, and turn off the instrument This ensures that the capillary will not dry out Data Analysis: Use peak area to calculate the percentage of each compound We did not use standard to determine migration time of each benzoic acid derivative Can you predict which is p-hydroxybenzoic acid and which is p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid? Ask experts, assistants, or Dr. Foy if you have any questions Data and Analysis Unfortunately, this is the data results for the CE. As you can see, the mixture results are not very good. We kept receiving error messages from the CE and they stated that the pressure was wrong. This kept delaying the experiment and the instrument would sporadically stop running. We got better results for the IC, which all the spectra containing the peaks, retention time, and heights and relative areas. This data is all included within my lab notebook for further analysis. For all of the spectra there are clear injection peaks along with distinguishable peaks. Conclusion This lab was not as fun as the other labs that have been done this year, however we did get good results for the IC. The CE did not give as good as results due to the constant pressure error and sporadic stopping of running the sample. The peaks showed good height, retention time and injection points which showed that we were running the experiment right. I don’t know why the separation did not work for mixture B that we did.