Carbohydrates Notes
advertisement

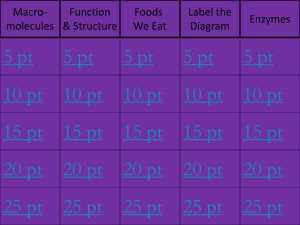
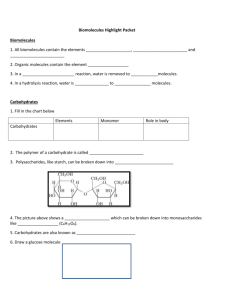
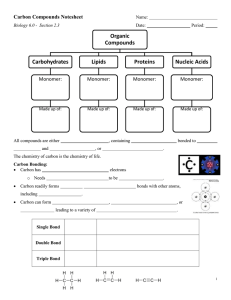
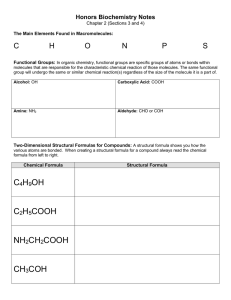
Name:________________________________________________Date:____________________Period:______ WNHS Honors Biology Biochemistry Notes What is biochemistry? I. Organic Compounds: Why is Carbon important? Four valence electrons strong covalent bonds 4 Major Types of Large Organic Compounds POLYMER 1. MONOMER Carbohydrates a. Structure – Elements: Monomer: b. Functions – Three classes of carbohydrates Monosaccharides: Examples: Disaccharides: Examples: Polysaccharides: Examples: 2. Lipids a. Structure – Elements: Monomer: b. Functions – Two Classes of Lipids: Triglycerides (Fats): Phospholipids: Saturated Fats: Unsaturated Fats: 3. Proteins a. Structure – Elements: Monomer: b. Functions – c. ENZYMES are proteins! Characteristics: Speed up reactions CATALYSTS lower the activation energy required for a reaction Specific: one enzyme for one reaction Reusable HYDROLYSIS DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS (Condensation Reaction) How they work: Enzymes have ________________ ____________ where the substance they catalyze can attach. That substance is called the _____________________. Their shapes match perfectly, like a lock and key. After the reaction, the substrate is released and the _____________________ does its job over again. Enzymes operate within an optimum ______________________ and pH range. Otherwise, they _____________________ (change their shape), which means the __________________________ they catalyze no longer matches their _________________ ________________. 4. Nucleic Acids a. Structure – Elements: Monomer: b. Functions – Two classes of nucleic acids: DNA RNA