10internationalfinancemultchoice
advertisement

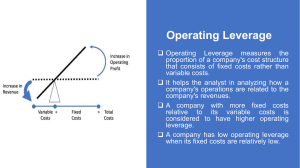
1. If I believe in the basic principle of a risk-reward relationship, my conclusion regarding security ratings and yields between an Aaa bond and a Baa bond would be that: the Aaa bond would have the lower yield. the Aaa bond would have the higher yield. the Baa bond would have lower default risk. default risks would differ but yields would be equal. 2. A firm's degree of operating leverage (DOL) depends primarily upon its sales variability. level of fixed operating costs. closeness to its operating break-even point. debt-to-equity ratio. 3. An EBIT-EPS indifference analysis chart is used for evaluating the effects of business risk on EPS. examining EPS results for alternative financing plans at varying EBIT levels. determining the impact of a change in sales on EBIT. showing the changes in EPS quality over time. 4. EBIT is usually the same thing as: funds provided by operations. earnings before taxes. net income. operating profit. 5. In the context of operating leverage break-even analysis, if selling price per unit rises and all other variables remain constant, the operating break-even point in units will: fall. rise. stay the same. still be indeterminate until interest and preferred dividends paid are known. 6. If a firm has a DOL of 5 at Q units, this tell us that: if sales rise by 5%, EBIT will rise by 5%. if sales rise by 1%, EBIT will rise by 1%. if sales rise by 5%, EBIT will fall by 25%. if sales rise by 1%, EBIT will rise by 5%. 7. This statistic can be used as a quantitative measure of relative "financial risk." coefficient of variation of earnings per share (CVEPS) coefficient of variation of operating income (CVEBIT) (CVEPS - CVEBIT) (CVEPS + CVEBIT) 8. A firm's degree of total leverage (DTL) is equal to its degree of operating leverage financial leverage (DFL). its degree of plus minus divided by multiplied by 9. The further a firm operates above its operating break-even point, the closer its degree of operating leverage (DOL) measure approaches minus one. zero. one. infinity.