Energy: Potential, Kinetic, Heat, Thermodynamics - High School Chemistry
advertisement

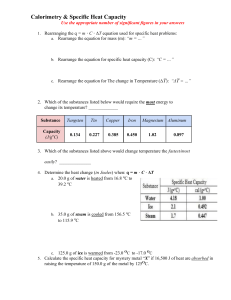
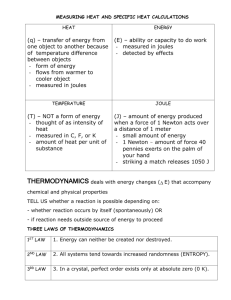
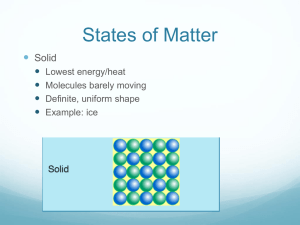
CHAPTER 10 ENERGY NATURE OF ENERGY Energy – the ability to do work May be potential or kinetic Potential energy is due to position or composition Kinetic energy is due to motion depends on mass and velocity KE=1/2 mv2 TEMPERATURE AND HEAT Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the random motions (thermal energy) of the components of a substance. Heat is the flow of energy due to temperature differences – flows from high to low Exothermic – energy released Endothermic – energy absorbed THERMODYNAMICS The study of energy Law of conservation of energy is often referred to as the First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic quantities have 3 parts: a number indicating magnitude of change, a sign ( + or -) indicating the direction of change, and a unit (J, kJ, cal, kcal) ENERGY CONVERSIONS Energy (heat) may be expressed in joules, kilojoules, calories or kilocalories. 1 calorie (cal) = 4.184 joules (J) How many joules in 60.1 calories? HOW MANY CALORIES IN 28.4 J? SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY Defined as the amount of energy required to change the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1oC Different substances have different specific heat capacities. Metals tend to have a low specific heat capacity compared to water – they tend to heat quickly and cool quickly, while water does not. CALCULATING ENERGY CHANGES How much energy is required to heat 25 g of liquid water from 25oC to 100.oC? Specific heat capacity of liquid water is 4.18 J/goC. Q = mcΔT Q (energy) = m(mass) x c(specific heat) x ΔT (change in temperature = Tf – Ti) Q = (25 g)(4.18 J/goC)(100.o – 25oC) If ΔT is positive, Q will be positive. If ΔT is negative, Q will be negative. How many joules of heat are given off when 5.0 g of water cools from 75oC to 25oc? (Specific heat of water = 4.18 J/goC) HEATING CURVE OF WATER ENERGY DURING PHASE CHANGE Energy is increasing/decreasing during phase changes even though temp. remains constant. Q = mass(m) x heat of fusion (Hf) for melting and freezing Q = mass(m) x heat of vaporization (Hv) for boiling and condensing Values will be positive for melting and boiling Values will be negative for freezing and condensing How many calories are given off when 85 g of steam condense to liquid water? (Hv= 539.4 cal/g) How many joules does it take to melt 35g of ice at 0oC? (Hf = 333 J/g) How many joules are required to convert 10.0g of ice at -10.0oC to steam at 150. oC? (specific heat of ice = 2.06 J/goC and specific heat of steam = 2.03 J/goC) A five step problem! YOUR ASSIGNMENT: Practice problems are in the yellow boxes. Page 329 Practice Problem 10.2 Page 330 Practice Problem 10.3 Page 332 Practice Problem 10.4 Page 333 Section 10.2 Review Questions 2-6