Taxonomy
advertisement

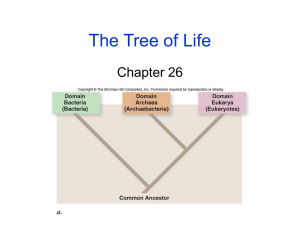
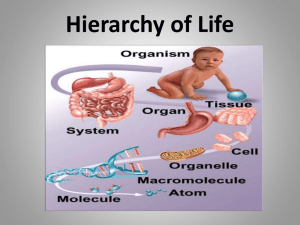
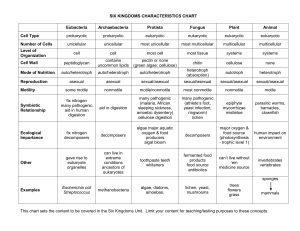
Classification & Taxonomy 10-1 An organized system to classify all living things Biology is the study of life… • But how do we know something is “alive”? – Metabolism • Consume molecules • Produce wastes • Exchange gases – Reproduction – Cells – DNA The Need for a Classification System… • Organizing and categorizing all of the organisms that exist on earth today is quite a task! A system of classification must be… - organized and logic - universal (used by all scientists) • Our current system breaks down organisms into more & more closely-related groups until only one group is left…the “species”! Taxonomy… • Taxonomy is the study, practice, and science of the classificiation of organisms. Binomial Nomenclature (“to name with 2 names”) • Each species is named with 2 words – The first word is the “genus” – The second word is the “specific epithet” – When written together, this name is called the “species” – Ex: Homo sapiens or Homo sapiens • Homo = genus of humans • sapiens = specific epithet of humans • Note: genus is capitalized, other is not…both underlined or italicized Taxons • Groups of related genera are classified together in the same family • Groups of related families for an order • This follows the pattern… Orders Class Phylum Kingdom • We usually memorize these from the largest to smallest direction: – KPCOFGS Test Yourself! Name the 7 major taxons in order… • • • • • • • Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Dichotomous Keys • Rules: – Always start at clue set #1 – One of the choices must be correct…the other must be incorrect – Identify the correct one and go where it says – When creating a key, it is better to use “is…is not” format for clues – Will always have one fewer clue than # of objects Dichotomous Key Example • Example: • 1. A. contains ink……………..…..go to 2 • B. does not contain ink………..go to 3 • 2. A. point made of metal………..pen • B. point not made of metal……marker 3. A. made of plastic…..mechanical pencil B. not made of plastic…...regular pencil All organisms have been placed into one of 6 kingdoms. • This is a generally agreed-upon standard, but is subject to change • We have not always had 6 kingdoms, and some scientists use fewer or more • What criteria are used to place an organism in a kingdom? Basic Criteria for Kingdoms (The Big 5!) 10-2 • # of Cells – Unicellular or Multicellular • Type of Cell – Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic • Cell Wall – Yes or No • Nutrition – Autotrophic or Heterotrophic • Motility – Yes or No Test Yourself! What do the following mean? • • • • • • • • • Unicellular Multicellular Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Autotrophic Heterotrophic Motile Nonmotile Cell Wall Bacteria • The Big 5: • K. Archaebacteria – – – – Harsh environments Methanogens (anerobic) Thermophiles (high heat) Halophiles (salt) • K. Eubacteria – “common” bacteria – Ex: E.coli; Staphylococcus aureus – Unicellular – Prokaryotic – The other 3 traits are variable… examples of bacteria exist for each trait K. Protista • The most diverse and oft-changing kingdom! • The Big 5: – Unicellular*** – Eukaryotic – The other 3 traits are variable…protists of various types exhibit both versions. K. Fungi • Often seem plant-like…but cannot make food! • The Big 5: – Multicellular – Eukaryotic – Cell wall – of chitin – Heterotrophic – absorb food – Nonmotile K. Plantae • Usually green due to chlorophyll • The Big 5: – Multicellular – Eukaryotic – Cell wall – of cellulose – Autotrophic – Nonmotile K. Animalia • Large, motile creatures that eat! • The Big 5: – Multicellular – Eukaryotic – No cell wall – Heterotrophic – ingest food – Motile Taxonomic Tree 10-3 • Cladistics- classification system based on phylogeny; assumes that as groups of organisms diverge and evolve from a common ancestral group, they retain derived traits. • Cladogram is the diagram used to represent the phylogeny of a species based on those derived traits. Taxonomic Tree Which group of organisms are most closely related? Butterflies, moths and flies X Y Z 1. A. Is multicellular………………………………..go to 2 B. Is unicellular……………………….…………go to 3 2. A. Contains chlorophyll; is green…………….Chlorella B. Contains erythrophyll; is red………………Hemalia 3. A. Cell is oblong with tiny cilia………………...Paramecium B. Cell is blob-like with slender extensions….Amoeba