Chemistry 222 - Test 2 Review Sheet
advertisement

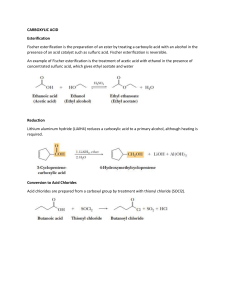
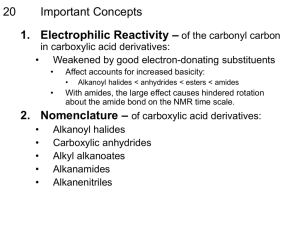
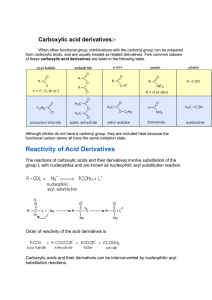
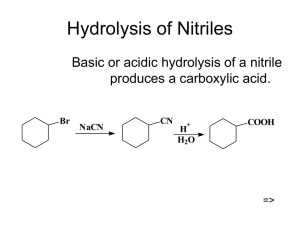
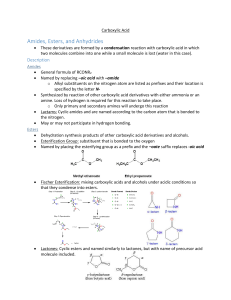
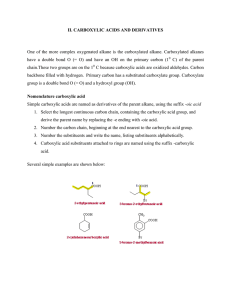
Chemistry 222 - Test 2 Review Sheet Naming Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, Acyl Chlorides, Acid Anhydrides, Carboxylate Salts, Esters, Amides Recognizing ethers, epoxides, crown ethers, thiols, sulfides, disulfides, sulfoxides, sulfones, sulfonic acids, aldehydes, hemiacetals, acetals, lactams, amines, imines, enamines, carboxylic acids, esters, thioesters, amides, lactones, lactams, anhydrides, acyl chlorides, imides Structures of pyridine, furan, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane Relative acidities of carboxylic acids. Relative acidities of alpha hydrogens in carbonyl compounds. Relative reactivities of acyl compounds in nucleophilic acyl substitution. Which of these reagents (1-7) would react with each of these molecules (a-e): 1) H2O ; 2) CrO3, H2SO4 ; 3) EtMgBr ; 4) LiAlH4 ; 5) Dess-Martin ; 6) Ph3P=CH2 ; 7) SOCl2 a) Alcohol; b) Ether; c) Aldehyde; d) Ketone; e) Carboxylic Acid; f) Ester Give the full name represented by these acronyms: DMSO; THF; MCPBA; DIBAH; NBS; TMS Using the Grignard Reaction and protecting groups make each of the substances on the right from the two substances on the left. (More than 1 step is required.) OH OH OH Br OH O O OH O How would you make each of the two starting materials above from an alcohol. (More than 1 step is required for halohydrin.) Write the mechanism for the reaction shown below: O O - Cl O O Fill in the missing starting materials, reagents, and products. 1) NaBH4 2) H 3O+ 1) DIBAH 2) H 3O+ TosCl OTos NaNH 2 pyridine Br 1) 2) H2O M gBr O 1) H2 N S NH2 2) H2O,NaOH