Biology Chapter 14 Vocabulary Review Sheet
advertisement

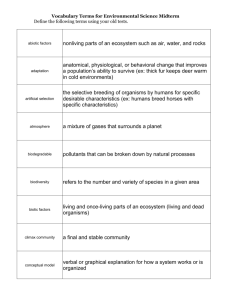
Name:__________________________________________ Biology Period___________ Date______________ Chapter 14 Key Vocabulary Review MATCHING Place the word and letter in the blank next to the correct definition. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. Habitat Ecological niche Competitive exclusion Ecological equivalents Competition Predation Symbiosis Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Population density Population dispersion Survivorship curve Letter Word n. o. p. q. r. s. t. u. v. w. x. y. z. Immigration Emigration Exponential growth Logistic growth Carrying capacity Population crash Limiting factor Density-dependent limiting factor Density-independent limiting factor Succession Primary succession Pioneer species Secondary succession Definition Way in which individuals of a population are spread out over an area or volume. Establishment and development of an ecosystem in an area that was previously uninhabited. Movement of individuals into a population. Environmental factor that limits the growth and size of a population. Process by which one organism hunts and kills another organism for food. Dramatic decline in the size of a population over a short period of time. Environmental resistance that affects a population regardless of population density. Reestablishment of a damaged ecosystem in an area where soil was left intact. Theory that states that no two species can occupy the same niche at the same time. Graph showing the surviving members of each age group of a population over time. Ecological relationship in which one species receives a benefit but the other species is not affected one way or another. Dramatic increase in population over a short period of time (Jshaped curve) Measure of individuals living in a defined area. Combined biotic and abiotic factors found in the area where an organism lives. Number of individuals that the resources of an environment can normally and persistently support. Ecological relationship in which two organisms attempt to obtain the same resource. Ecological relationship between members of at least two different species that live in direct contact with one another. Environmental resistance that affects a population that has become overly crowded. Ecological relationship between two species in which each species gets a benefit from the interaction. Movement of individual out of a population. All of the physical, chemical, and biological factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy, and reproduce in an ecosystem. Sequence of biotic changes that regenerate a damaged community or start a community in a previously uninhabited area. Population growth that is characterized by a period of slow growth, followed by a period of exponential growth, followed by another period of almost no growth (S-shaped curve). Organisms that share a similar niche but live in different geographical regions. Organism that is the first to live in a previously uninhabited area. Ecological relationship in which organism benefits by harming another organism.