Read Sections…
advertisement

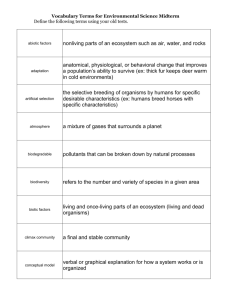
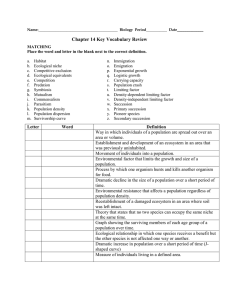
Road Map – Ecology (Part 2) Biomes and Population Growth 4.2 – What Shapes and Ecosystem 1. 2. 3. Describe how biotic and abiotic factors influence an ecosystem. Describe the interactions that occur within an ecosystem. Describe the phenomenon of ecological succession. Read Sections… Biotic and Abiotic Factors The Niche Community Interactions Ecological Succession 4.3 – Biomes 1. Describe the unique characteristics of each of Earth’s biomes. Read Sections… Biomes and Climate The Major Biomes Other Land Areas 5.1 – How Populations Grow 1. 2. 3. Describe the characteristics of a population List the factors that affect population size Distinguish between exponential growth and logistical growth Read Sections… Characteristics of Populations Population Growth Exponential Growth Logistic Growth 5.2– Limits to Growth 1. Describe the factors that limit the growth of a population Read Sections… Limiting Factors Density-Dependent Factors Density-Independent Factors 5.3– Human Population Growth 1. Describe the factors that limit the growth of a population Read Sections… Historical Overview Patterns of Population Growth Future Population Growth 1. biotic factor: 2. abiotic factor: 3. habitat: 4. niche: 5. resource: 6. competitive exclusion principle: 7. predation: 8. symbiosis: 9. mutualism: Vocabulary biological influence on organisms within an ecosystem physical, or nonliving, factor that shapes an ecosystem the area where an organism lives, including the biotic and abiotic factors that affect it full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which an organism uses these conditions any necessity of life, such as water, nutrients, light, food, or space ecological rule that states that no two species can occupy the same exact niche in the same habitat at the same time interaction in which one organism captures and feeds upon another organism relationship in which two species live closely together symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit from the relationship 10. commensalism: 11. parasitism: 12. ecological succession: 13. primary succession: 14. pioneer species: 15. secondary succession: 16. biome: 17. tolerance: 18. population density: 19. 20. 21. immigration: emigration: exponential growth: 22. logistic growth: 23. carrying capacity: 24. limiting factor: 25. density-dependent limiting factor: 26. predator-prey relationship: 27. density-independent limiting factor: 28. microclimate: 29. canopy: symbiotic relationship in which one member of the association benefits and the other is not helped or harmed symbiotic relationship in which one organism lives in or on another organism (the host) and consequently harms it gradual change in living communities that follows a disturbance succession that occurs on surfaces on which no soil exists first species to populate an area during primary succession succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and dominant communities the capacity of an organism to grow and thrive when subjected to an unfavorable environmental factor number of individuals per unit area movement of individuals into an area movement of individuals out of an area occurs when individuals of a population reproduce at a constant rate occurs when the exponential growth of a population slows or largest number of individuals an area can support when limiting factors kick in a factor that causes population growth to slow down or stop slows or stop population growth only when the population density reaches a certain level the regulation of population size by predators affect all populations in the same way, regardless of their size (e.g. drought, heat, cold, tornadoes) climate within a small area that differs significantly from the climate of the surrounding area dense covering formed by the leafy tops of 30. understory: 31. deciduous: 32. coniferous: 33. humus: 34. taiga: 35. permafrost: tall trees in a rain forest layer in a rain forest formed by shorter trees and vines term used to refer to refer to a tree that sheds its leaves during a particular season of each year term used to refer to trees that produce seed-bearing cones and that have thin leaves shaped like needles material formed from decaying leaves and other organic material biome in which the winters are cold but summers are mild enough to allow the ground to thaw layer of permanently frozen subsoil in the tundra