Notes
advertisement

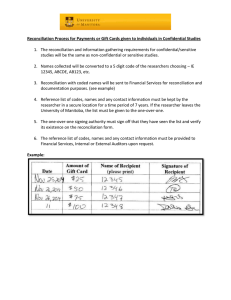
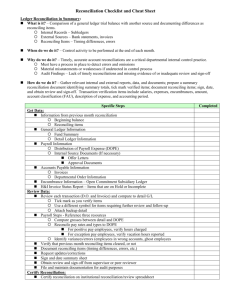
College Accounting Chapter 8: Cash and Internal Controls (Notes) Name _____________________________ I. INTERNAL CONTROL A. Purpose of Internal Control An internal control system consists of policies and procedures managers use to: 1. 2. 3. 4. B. Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX) What does it require? ________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ C. Principles of Internal Control (list for sure & take notes as needed) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The __________________________________________ provides a framework for how these principles improve the quality of financial reporting. D. Technology and Internal Control Technology provides quick access to databases and information. Examples of how technology impacts internal control: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. E. Limitations of Internal Control Examples of Human error: ________________________________________________________ What drives fraud? ______________________________________________________________ Explain the cost-benefit principle ____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ II. CONTROL OF CASH – Basic guidelines for control of cash and cash equivalents include: 1. 2. 3. A. Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Liquidity 1. What is liquidity? 2. What is a demand deposit? 3. What is a time deposit? 4. What are cash equivalents? 5. What two criteria must they meet? Note: Only investments purchased within three months of their maturity dates usually satisfy these criteria. B. Cash Management 1. Goals of Cash Management a. b. 2. Effective cash management principles: a. b. c. d. e. C. Control of Cash Receipts Procedures for protecting cash received over-the-counter and by mail: 1. 2. D. Control of Cash Disbursements To safeguard against theft: 1. 2. 3. Use a voucher system of control that establishes procedures for: a. b. 4. Use a petty cash system of control as follows: a. b. c. d. III. BANKING ACTIVITIES AS CONTROLS A. Basic Bank Services Bank accounts permit depositing money for safeguarding and helps control withdrawals. Electronic Funds Transfer is __________________________________________________________________ B. Bank Statement Shows activities of a bank account and is used to prove the accuracy of the depositor’s cash records in preparing a bank reconciliation. 1. What is a bank reconciliation? 2. Factors causing the bank statement balance to differ from the depositor’s book balance are: a. b. c. d. e. 3. Steps in preparing the bank reconciliation: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. 4. Adjusting entries from a bank reconciliation a. What is it important to remember about adjusting? b. All reconciling additions to book balances do what to cash? Debit / Credit c. All reconciling subtractions to book balances do what to cash? Debit / Credit