The Urinary System
advertisement

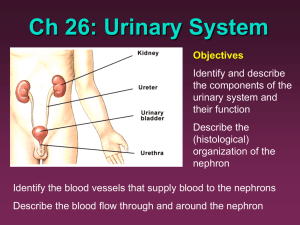
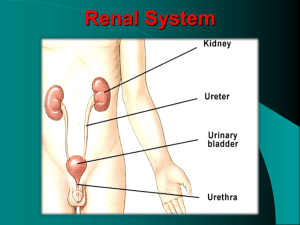
THE URINARY SYSTEM Chapter 26 OBJECTIVES Describe the functional organization of the urinary system. Explain how the kidneys remove metabolic products from the circulation to produce urine. Labs Macroscopic – Kidney Dissection Microscopic – Kidney slide investigation Urinalysis Activity/Reading Kidney Stones 3 PRIMARY FUNCTIONS excretion: removal of organic waste products from body fluids elimination: the discharge of wastes products into the environment homeostatic regulation: control the volume and solute concentration of blood plasma VOCABULARY kidneys urine urinary tract ureters urinary bladder urethra micturition (urination) fibrous capsule perinephric fat capsule renal fascia hilum KIDNEYS ARE HIGHLY VASCULAR STRUCTURES CONTAINING FUNCTIONAL UNITS CALLED NEPHRONS – THEY PERFORM FILTRATION, REABSORPTION AND SECRETION left kidney lies slightly superior to the right kidney between T-12 and L-3 (see page 231) Fig 26-2 Each kidney basically hangs suspended by collagen fibers from the renal fascia and is packed in a soft cushion of adipose tissue “floating kidney”???? THE KIDNEY a typical adult kidney is reddish-brown 4 in x 2.2 in x 1.2 in weighs about 150 g (5.25 oz) Fig 26-3 Fig 26-4 BLOOD SUPPLY Each kidney receives blood through a renal artery Eventually reaches afferent arterioles which deliver blood to the capillaries (of glomerulus) supplying individual nephrons Blood leaves the glomerulus in efferent arterioles and drains into small venules The blood eventually drains directly into the renal vein Fig 26-5 (c) INNERVATION kidneys and ureters are innervated by renal nerves renal nerves – enter each kidney at the hilum and follow the tributaries of the renal arteries to reach individual nephrons Sympathetic innervation: adjusts rate of urine formation by changing blood flow and blood pressure at the nephron stimulates the release of renin, which ultimately restricts the loss of water and salt in the urine by stimulating reabsorption at the nephron