Excretion and Osmoregulation Questions
advertisement

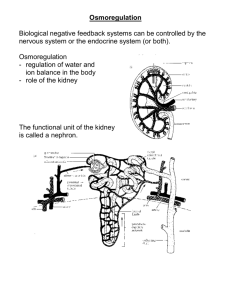
Excretion and Osmoregulation Questions 1. Which region of the kidney contains the Malpighian bodies, and which region the loop of Henle and the collecting ducts? 2. Urine is carried first to the bladder thence onwards to the exterior of the body. What is the name of the tube in each case? 3. Most nephrons of the human kidney are cortical a. What is a juxtamedullary nephron? b. Under which environmental conditions are animals most likely to have evolved juxtamedullary nephrons? 4. Where does ultrfiltration occur in the vertebrate nephron? What is the source of energy for ultrafiltration? 5. Which components of the body are normally never found in the filtrate of the renal capsule? 6. List the main components of the blood which are likely to be filtered in the nephron. Which of these are likely to be re-absorbed in the renal tube? What are the energy sources for these two processes? 7. The cells of the proximal convoluted tubule have brush borders. What dos this mean and what advantage does it confer? 8. List, in order the pathway blood takes as it passes through the kidney. 9. What is the effect of ADH on the permeability of the walls of the collecting ducts? In what circumstance in the body is ADH released? 10. Why is an anticoagulant needed in the process of withdrawing blood fr dialysis? 11. How is it possible for the dialysate to be used to withdraw excess water from the blood? 12. What advantage arises from arranging for blood and dialysate to flow in opposite directions in the kidney machine? 13. In what form do fresh water fish get rid of their waste. Explain why it is possible for them to excrete nitrogenous waste in this form. 14. Marine bony fish tissue fluid is hypotonic to the sea water, what will this cause to happen and how does the fish get around the problem? 15. Cartilaginous marine fish store urea in their blood in order to keep their tissue fluid isotonic to the surrounding water. What does this mean? Why is it not possible for humans to do this?