The Urinary System
advertisement

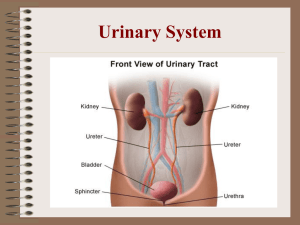
The Excretory System Functions • Excretion - Filtering metabolic wastes • Wastes – Excess salts – Carbon Dioxide – Urea – produced when amino acids are used for energy Skin • Sweat – Excess water, salt, small amounts of urea Lungs • Excrete CO2 when energy is produced by the mitochondria Liver • Converts amino acids to useful compounds • Produces urea as waste Kidneys • Remove waste products from the blood • Maintain blood pH • Regulate water content of blood Urinary System The Urinary Organs: • Kidneys: filters that take waste out of the blood and make urine The Urinary Organs: • Ureters: tubes that carry urine to the bladder The Urinary Organs: • Bladder: a muscular bag that collects urine The Urinary Organs: • Urethra: a tube that carries urine out of the body Kidneys Kidney Regions Renal Cortex Renal Medulla Renal Pelvis Blood Flow • Waste-laden blood enters kidneys through the renal artery • Clean filtered blood leaves the kidney through the renal vein Nephron • Structural units of the kidney • Over 1,000,000 in each kidney! – 3 cm long – 0.03 mm wide • Filter the blood • Reabsorb water, glucose, and salt Glomerulus Nephron Glomerulus Loop of Henle Bowman’s Capsule Filtration • Blood pressure forces blood through the glomerulus – All blood is filtered every 45 minutes Filtration • Filtrate – Water, urea, glucose, salts, amino acids, and some vitamins • Proteins, cells, and platelets are too large to pass through and remain in the blood Reabsorption • Most of the filtrate reenters the blood • Active transport – Amino acids, fats, glucose • Osmosis – 99% of water reabsorbed Urine • Forms in Kidneys – Loop of Henle • Made up of urea, excess salts, and water – Concentration variation • Kidney Ureter Bladder Bladder • Hollow muscular organ • Flexible cells • Nerves tell the brain when the bladder is full. – After 200 ml have accumulated – After 1 minute reflex subsides • Holds approximately 500 ml Kidney Disease Dialysis • http://www.kidneypatientguide.org.uk/site /HDanim.php