The Skeleton
advertisement
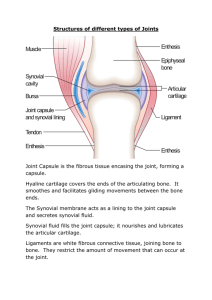
The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeleton • Support • Allows movement • Protection Joints • This is where two or more bones meet. • Most joints allow movement to take place. • Types of Joints: 1. Fixed / immovable 2. Synovial / freely moveable 3. Gliding joint 1. Fixed joints/ Immovable Where there is no movement between bones –skull. 2. Freely moveable or synovial joints which are of two types: • Ball and socket joints which allows movement in all directions – shoulders and hips. • Hinge joints which allows movement in one direction only – elbow and knee Cartilage – protects ends of bones and reduces friction in the joint. Synovial fluid – lubricate the joint and allows joint to move more freely. 3. Gliding Joint • The bones side across each other • Example: Wrist • (no diagram needed) Tendons and Ligaments • Tendons – connect muscle to bone. • Ligaments – connect bone to bone. Tendons – connect muscle to bone Ligaments – connect bone to bone. Muscles • Muscles are protein structures that can contract. • They cause bone to move. Antagonistic Muscles • Pairs of muscles which pull in opposite directions to bring about movement – biceps and triceps in arm. Watch the muscles…. Watch the muscles…. Watch the muscles…. Watch the muscles….