Cardiovascular Disease
advertisement
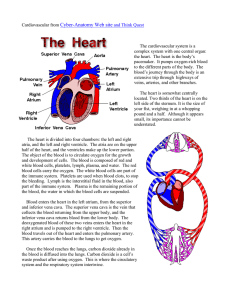
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Your “real” heart HEART The muscular pump that makes the cardiovascular system work. It is made up of cardiac muscle and provides the power needed for life. Your heart will beat an average of 2 ½ billion times in a lifespan. You have approximately 5 liters of blood in your body Essential question – What is the function of the heart? To pump blood to all parts of the body providing food and oxygen to all its cells. BLOOD Blood is the fluid of life. It transports oxygen and carbon dioxide, nourishment, and disease fighters to all parts of the body. PLASMA The liquid portion of the blood in which all other cells, nutrients, and hormones are suspended. Plasma is 90% water TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS RED CELLS – carry oxygen to all parts of the body. HEMOGLOBIN is the protein in RBC’s that the O2 combines to. It give blood its red color. WHITE BLOOD CELLS – are part of your immune system and fight disease. PLATELETS – clot your blood to stop bleeding. BLOOD VESSELS – YOUR TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM ARTERIES Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart Two major/important arteries are: Aorta – largest artery in body that takes blood away from the heart Pulmonary Arteries – carry ‘unoxygenated’ blood away from heart and to the LUNGS to pick up O2. VEINS Veins return unoxygenated blood back to the heart. Two major veins are: Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava CAPILLARIES – smallest vessel in the body, where O2 & CO2 is exchanged BLOOD PRESSURE The force of blood against the arterial walls 120/80 is an average BP HYPERTENSION = a high blood pressure count YOUR “PULSE” The number of times your heart beats per minute. The average heart beats 70-80 times in 60 seconds. Your heart is a muscle, so if you exercise it (aerobically), your heart will get stronger and not have to work so hard. A trained athlete’s heart would beat LESS than 70-80 times. HEART ANATOMY HEART ANATOMY TERMS Atrium – the upper / receiving chambers of the heart Ventricle – the lower / pumping chambers of the heart Valves – tiny flaps of skin that open and close like one-way doors Septum – the muscular wall that divides the heart into a right and left side TYPES OF CIRCULATION PULMONARY CIRULATION – BLOOD THAT FLOWS FROM THE HEART – TO THE LUNGS – BACK TO THE HEART SYSTEMIC – BLOOD THAT FLOWS TO EVERY SINGLE PART OF THE BODY except the lungs CORONARY – SUPPLIES BLOOD ONLY TO THE HEART