File - Dado Science
advertisement

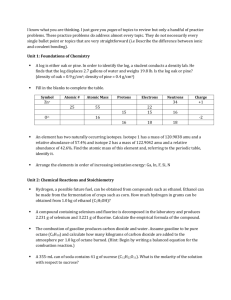
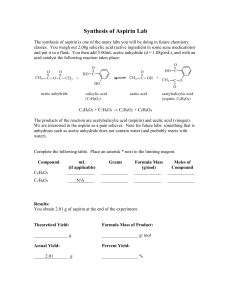
Titration of Aspirin Lab Data Table: Trial Concentration of NaOH (M) 1 Initial Final Volume Volume Reading Reading NaOH (mL) NaOH (mL) Volume of NaOH used to Titrate (mL) Volume NaOH (L) Concentration of Aspirin (M) Mass of Aspirin (g) 0.100 2 0.100 3 0.100 Average Post Lab Calculations: 1. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) and sodium hydroxide. 2. For each trial, calculate the concentration of aspirin and the mass of the aspirin then calculate the average. Show your work for one trial. 3. According the label on the bottle of aspirin, each tablet contains 325mg of aspirin. Calculate the percent error using your average mass of aspirin from the lab. Post-Lab Analysis: 1. What is the purpose of the indicator, phenolphthalein, in an acid-base titration? 2. How could the insoluble white binder affect the detection of the end point in this experiment? 3. The parietal cells of the stomach secrete hydrochloric acid at a concentration of 0.16M. Tums is a common antacid used to neutralize stomach acid which can cause heartburn and indigestion. One tablet contains 0.05M of calcium carbonate in a 0.005L tablet. How much stomach acid will one Tums tablet neutralize?