D A T AS4
advertisement

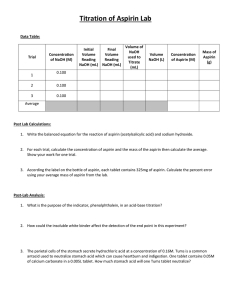
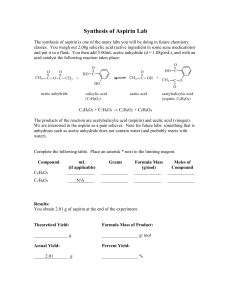
DETERMINATION OF ASPIRIN IN TABLETS AS4 Last Revised: May 2015 1. REAGENTS & EQUIPMENT 1.1 Hydrochloric acid (0.2 M) 1.2 Sodium hydroxide solution (0.2 M) 1.3 UV/VIS spectrophotometer 1.4 Methanol 1.5 250 mg/L aspirin standard in methanol (including 0.1% citric acid) 1.6 Philips non‐scanning PU8625 UV/VIS spectrophotometer 2. PROCEDURE 2A. Sample preparation 2.1 Check the packet for the expected mass of aspirin per tablet. 2.2 Weigh accurately three tablets and calculate the average mass. 2.3 Devise a scheme for obtaining triplicate sample masses containing approximately 25 mg of aspirin. 2.4 Check with this with your teacher. 2.5 Rinse three 50 mL volumetric flasks with methanol. 2.6 Weigh accurately three samples and transfer to the rinsed flasks. 2.7 Add approximately 30 mL of methanol to each, cap and shake well for 2 minutes. Make up to the mark with methanol. 2.8 Pipette 5 mL of each sample solution into separate 100 mL volumetric flasks. 2.9 Add 25 mL (by measuring cylinder) of 0.2 M NaOH to each flask. 2.10 Allow to stand for 30 minutes. 2.11 Make each flask up to the mark with 0.2 M HCl. 2B. Standard preparation 2.12 Pipette 5, 10 and 20 mL of the stock aspirin standard into separate 100 mL volumetric flasks. 2.13 Add 25 mL (by measuring cylinder) of 0.2 M NaOH to each flask. 2.14 Prepare a blank by adding mixing 25 mL of 0.2M NaOH with 50 mL of 0.2 M HCl, then add 5 mL of one of the samples. 2.15 Allow to stand for 30 minutes. 2.16 Make each flask up to the mark with 0.2 M HCl. 2C. Analysis The analysis will be done at 302 nm. What cell is appropriate? You are required to use the Philips PU8625 instrument. 2.17 Set it up for measurement at 302 nm and zero with a blank in the chosen cell. 2.18 Measure the absorbance of each standard, sample and recovery check. 2.19 Re‐measure the first solution (standard or sample) analysed. REPORT Calculations Standards 1. Calculate the concentration of aspirin of the standards after dilution in the 100 mL flasks. 2. Plot a calibration graph from the standards. Samples 3. Determine the concentration in mg/L for each sample. 4. Apply the appropriate dilution factor. 5. Calculate the mass of analyte in the original 50 mL flasks. 6. For each analysed portion, calculate the mg aspirin/tablet for each using the formula below. mg per tablet m xm m where ma is the mass of aspirin in the analysed sample mass mt is the average tablet mass ms is the sample mass 7. Calculate the average amount of aspirin/tablet. Discussion explain the reason for the samples being treated with NaOH solution and allowed to stand for 30 minutes explain why the samples are then acidified explain why salicylic acid would interfere with the analysis of aspirin Questions 1. What is the structure of aspirin? How does it differ from salicylic acid? 2. What is the natural source of salicylic acid? Reference: Sanyal & Dutto, Journal of AOAC International, Vol. 79(6), (1996) pp 1303‐05. There is a guide to this Exercise, including help with the calculations, on the website. AS4 p2 AS4. DETERMINATION OF ASPIRIN IN TABLETS RESULTS SHEET Manufacture ID code Tablet masses (g) Average Aspirin/tablet Sample mass to yield 25 mg analyte Mass (g) Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Abs. Standard 1 Standard 2 Standard 3 Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3