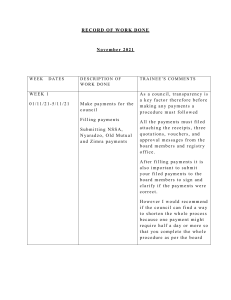
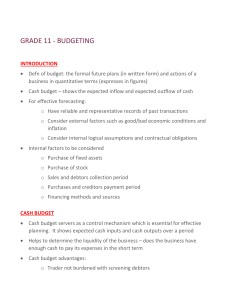
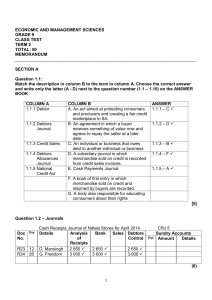
4. Managing cash flow
advertisement

Managing cash flow problems Problem - Insufficient working capital Low cash figure Insufficient cash available to pay for supplies and other day-to-day expenditures. Possible cause - Overtrading (the business has lots of orders and purchases supplies to meet them on credit. However, cash form sales does not arrive quickly enough to pay suppliers). This can lead to bankruptcy. Possible solution - Inject new capital (long-term finance) eg via a loan, or else slow the rate of growth. Low debtors figure Not usually a problem, but could indicate low sales figures if credit offers to customers prove unattractive. Possible solution – Introduce attractive trade credit terms to increase sales. Low stock Low raw material or component stock levels - may interrupt the production process. Delays will add to costs. Low stocks of finished products - delays in responding to orders from customers. Also, potential sales are lost. Possible causes - lack of cash or credit to purchase stock, or deliberately reducing levels below an optimal point. Solution – Improve efficiency of stock control system (eg JIT) or purchase more stock. High creditor figure The business owes large sums to creditors who may refuse to supply the business in future if they are not paid on time. Banks may demand repayment of overdrafts, and firms operating close to overdraft limits may not be able to cope with additional unforeseen demands for cash. Possible causes - Over-reliance on trade credit and shortterm financing eg overdrafts (which are repayable upon demand). Possible solution – Raise finance eg via a loan to pay debts Problem - Excessive working capital High stock Adds to costs (eg storage, insurance, depreciation due to obsolescence etc). Possible causes - over-stocking (allowing stock levels to build up), eg following a downturn in demand a firm might fail to reduce production levels, leading to higher stock levels. Possible solutions - Allow stocks to be sold without replacing them (running down stock). This will generate cash without increasing creditors. High cash There is an opportunity cost of holding excessive cash – the money could be used elsewhere in the business Possible solution - Excess cash can be released to pay off long term debts, purchase fixed assets, deposited in a high-interest savings account, or returned to the owners of the business eg via a dividend payment. High debtors Debtors may be taking longer to repay debts (results in lost interest the business could be receiving). Also, added costs of chasing up debtors. Possible causes - Poor debt collection, or poor screening of credit customers? Possible solutions - Chase over-due payments and begin credit checks. Other causes During a recession debtors may be late with payments as they try to improve their own cash flow situations. Seasonal demand. At times of peak demand firms need to ensure they carry enough stock to meet the needs of customers (eg toy manufacturers at Christmas). They may have difficulty paying suppliers earlier in the year due to low sales at time. Cash flow imbalances A business may have sufficient working capital on paper, but it may consist mainly of stock or debtors. The firm could therefore still have difficulty meeting its short-term liabilities. In this case cash levels can be increased by reducing stock & chasing up debtors. Firms with high cash levels but low stock may experience production problems.