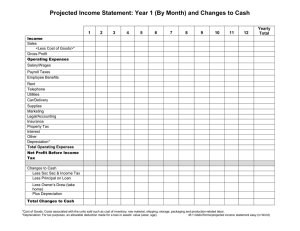
GRADE 11 - BUDGETING INTRODUCTION Defn of budget: the formal future plans (in written form) and actions of a business in quantitative terms (expresses in figures) Cash budget – shows the expected inflow and expected outflow of cash For effective forecasting: o Have reliable and representative records of past transactions o Consider external factors such as good/bad economic conditions and inflation o Consider internal logical assumptions and contractual obligations Internal factors to be considered o Purchase of fixed assets o Purchase of stock o Sales and debtors collection period o Purchases and creditors payment period o Financing methods and sources CASH BUDGET Cash budget servers as a control mechanism which is essential for effective planning. It shows expected cash inputs and cash outputs over a period Helps to determine the liquidity of the business – does the business have enough cash to pay its expenses in the short term Cash budget advantages: o Trader not burdened with screening debtors o Less administrative work – no need to maintain and monitor debtors ledger o Positive impact on working capital – cash received immediately therefore not tied up in working capital o Cash flow position of company is improved – no waiting period for payment o No possibility of bad debts as no debtors CREDIT CONSIDERATIONS With credit terms and budgets: o Consider payment terms and trends of both debtors and creditors o Consider if terms are complied with – ie payments are made when they are supposed to be made o Consider discounts offered and received STOCK CONSIDERATIONS Variable base stock o stock on hand varies from month to month o to determine stock to be purchased, cost of sales for current or future months is used Fixed base stock o Stock is maintained at a fixed value o Stock is replenished to this amount monthly and is based on cost of sales in current month o Implies that cost of sales = total stock purchases for the month o USED by Schools 2 PROJECTED INCOME STATEMENT Cash budget looks at future inflows and outflows of cash Projected income statement looks at expected income (revenue) and expenditure during the budget period Statement shows expected net profit in the future Following is needed: o Income statement for past year/month o Expected monthly sales figure or growth rate o Percentage gross profit margin on cost of sales or turnover o Expected other income o Expected operating expenses o Expected interest payable on loans o Expected non-cash expenses such as depreciation and bad debts Projections Reason What is does 3 Cash Budget Projects monthly cash receipts and cash payments over the budget period A planning instrument used by management to monitor whether the business is on track without running out of cash resources NO non-cash items are included (eg bad debts, depreciation) Include planned capital income and capital expenses (eg cash deposit on vehicle, cash for sale of assets, capital contributions) Determines cash surplus/shortfall and projected monthly bank balance over budget period Projected Income Statement Projects monthly profits/losses over the budget period A Include non-cash items (eg bad debts, depreciation) NO capital items included (eg capital contributions, fixed assets bought/sold) Determines the projected monthly net profit/loss over the budget period