Forecasting Industry Profitability
advertisement

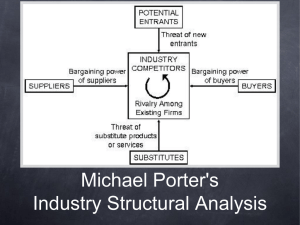
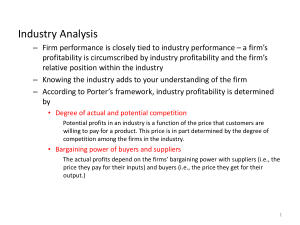
Team 4: Peter Hogue, Cameron Lloyd, Breann Flores, Jonathon Jordan, Defined as: All of the external influences that affect its decisions and performance. There are a large number of the influences so it helps to categorize them. 2 ways of classifying influences ◦ Source: political, economic, social and technological factors (PEST analysis) ◦ Proximity: “Micro Environment” can be distinguished from the “Macro Environment” 4 factors examined in a PEST Analysis ◦ Political: How the government restricts your product and how they select who is allowed to do what ◦ Economic: How the current economy affects business. (America’s recent recession) ◦ Social: How people view your product. Safety, fashion, etc. ◦ Technological: Are you staying ahead of the curve? Formed by relationship with three sets of players ◦ Customers: Firm must understand its customers in order to create value for them. ◦ Suppliers: Firm must understand suppliers and manage relationships with suppliers ◦ Competitors: Firm must understand competitors, because their profitability depends on it. To have profit in a firm, value has to be created for the customer. But, value doesn’t directly equal profit. Consumer surplus vs. producer surplus The value of the product to customers The intensity of competition The bargaining power of the producers in relation to their suppliers Some industries earn high rates of profit Others earn much lower rates of profit Small markets vs. large markets Three stages to predict future profitability of an industry 1.) examine current levels of competition and profitability 2.) Identify trends that are changing in the industry 3.) Identify how these structural changes will affect the five forces of competition and resulting profitability of the industry “ The threat of entry rather than actual entry may be sufficient to ensure that established firms constrain their prices to the competitive level” Contestability Sunk costs “hit-and-run” entry Barrier to entry Capital requirements Absolute cost advantage Product differentiation Government and legal barriers Retaliation Input market firms Output markets firms Buyers price sensitivity Bargaining power Concentration Concentration ratio Diversity of competitors Product differentiation Excess capacity and exit barriers Cost conditions Buyer propensity to substitutes Relative prices and performance substitutes Cigarettes example Wind farms vs. Natural gas Horizontal Competition ◦ Competition from substitutes ◦ Competition from entrants ◦ Competition from established rivals Vertical Competition ◦ Power of suppliers ◦ Power of buyers Availability of substitutes ◦ Ex. Coke and Pepsi Absence of close substitutes ◦ Ex. Gasoline ◦ Ex. Cigarettes Impact of the internet ◦ Ex. Travel agencies ◦ Ex. Telecommunications Capital requirements Economies of scale Absolute cost advantage Product differentiation Access to distribution channels Government and legal barriers Retaliation by established producers Concentration Diversity of competitors Product differentiation Excess capacity and exit barriers Cost conditions Bargaining Power ◦ Supplier ◦ Buyer Complex component manufacturers ◦ Ex. Disk drives Buyers’ Price Sensitivity ◦ Cost of product relative to total cost ◦ Product differentiation ◦ Competition between buyers Relative Bargaining Power ◦ Size and concentration of buyers relative to producers ◦ Buyers’ switching costs ◦ Buyers’ information ◦ Buyers’ ability to backward integrate To survive and prosper in an industry, a firm must meet two criteria: first it must supply what customers want to buy; second it must survive competition. Who are our customers and what do they want? What does the firm need to do to survive competition? Key Success Factors Combining the industry competition analysis with what the customers want we can discover what the key success factors are Prerequisites for success What do customers want? How does the firm survive competition? Analysis of demand •Who are our customers? •What do they want? Key Success Factors Analysis of competition •What drives competition? •What are the main dimensions of competition •How intense is competition? •How can we obtain a superior competitive position? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zrnPbZVlL QI Steel What do customers want? How do firms survive competition? Key success factors? •Low price •Product consistency •Reliability of supply •Specific technical specifications for special steel •Commodity products, excess capacity, high fixed cost, excess capacity, intense price competition •Cost efficiency and financial strength essential •Cost efficiency requires: large-scale plants, low-cost location, rapid capacity adjustment •Alternatively high technology, small-scale plants can achieve low costs through flexibility and high productivity Questions?