Industry Analysis Team 3: Jordan Myers, Jayson Davidson, Nick Thomas,

Industry Analysis
Foundations of Strategy
Team 3: Jordan Myers,
Jayson Davidson, Nick Thomas,
Phoenix Delcueto, Sienna Rucker
Topics
PEST
CASE: Mobile Phones
PORTERS 5 FORCES
ANALYZING INDUSTRY
APPLY INDUSTRY ANALYSIS
KEY ISSUES/CHALLENGES
KEY SUCCESS FACTORS
Environmental Scanning
Business Environment: external influences that affect its decisions
PEST Analysis
Porter's Five Forces
PEST Analysis
Political: rules and regulation from government
Economic: inflation, unemployment and growth rate
Social: Demographics and culture
Technological : keeping up with innovation
Opening Case: Mobile Phone Industry
Industry Growth of 50% throughout the 1990’s
Two major issues
Product Differentiation
Finding balance in bargaining power between handset manufacturers and service providers
PEST Analysis Case 2.1
Mobile Phone Industry
Political
Standardization
Licences
Economic
Mobile Phones in Developing Countries
Social
Health Scares
Changes in Fashion
Technological
Constant Innovation
PEST Analysis: Fluor Corp.
Political
Nuclear Regulatory Commision
Licences
Economic
Decrease in Metal Prices
Decrease in Oil Prices
Social
Considers Itself Responsible for Health, Safety and Environment
Fukushima Nuclear Disaster
Technological
New Nuclear Tech
Porter’s Five Forces
• Michael Porter created five forces framework that describes the industry structure
• Porter says that “thinking about firms as competing with rivals is too narrow”
• Porter’s five forces of competition framework views the profitability as determined by five sources of competitive pressure
Porter’s Five Forces of Competition
• Horizontal Sources of Competition
• Competition from substitutes
• Competition from entrants
• Competition from established rivals
• Vertical Sources of Competition
• Power of suppliers
• Power of buyers
Competition from Substitutes
• Are there substitutes available for our product or service ?
• The price customers are willing to pay for a product depends on the availability of substitute products
Competition from Substitutes
The absence of close substitutes for a product means that consumers are comparatively insensitive to price.
The existence of close substitutes means that customers will switch to substitutes in response to price increases
Fluor-Competition from Substitutes Analysis
Similar construction companies available
The Threat of Entry
• How easy will it be for someone to do what we are doing?
• When an industry earns a return on capital in excess of its cost of capital it will attract outside firms to the industry
• The number and level of barriers to entry in an industry determines how easily a new firm can enter the industry and begin to steal some of the shares of profit
The Threat of Entry- Barriers to Entry
• The barriers to entry in an industry include:
• Capital Requirements
• Economies of scale
• Absolute cost advantages
• Product differentiation
• Access to channels of distribution
• Governmental and legal barriers
• Retaliation
Fluor- Threat of New Entrants Analysis
Capital requirements to license engineers in each location they work in
A lot of governmental regulations that small firm can’t comply with
Competition Between Established Rivals
• How intensely do we compete in our industry?
Competition Between Established Rivals
Price Wars
Advertising and Innovation
Competition Between Established Rivals
• The intensity of competition depends on these factors:
• Concentration
• Di v ersity of competitors
• Product differentiation
• Excess capacity and exit barriers
• Cost conditions
Competition Between Rivals
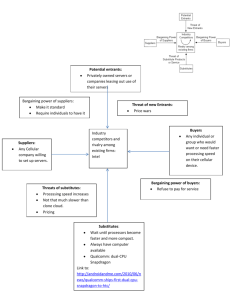
Fluor
Bargaining Power of Buyers
• How much influence do our customers have on our product and selling decisions?
Bargaining Power of Buyers
• The strength of buying power that firms face from their customers depends on two sets of factors:
• Buyers’ price sensitivity
• Relative bargaining power
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Fluor
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Questions to Ask:
• How much influence do our suppliers have on our product and selling decisions?
• Can we easily acquire our inputs from another source?
Applying Industry Analysis
Forecasting Industry Profitability a. Examine an industry’s current and recent levels of competition and profitability of its present structure.
b. Identify trends that change the industry’s structure: Consolidation, New Entrants,
Product differentiation / commoditization,
Affects on Demand.
c. Identify how structural changes will affect the five forces of competition and resulting profitability of the industry.
“Industry analysis is not about explaining the past, but to predict the future.”
Applying Industry Analysis (continued…)
Positioning the Company
Example: Demographics of Music Purchases
Example: PACCAR Fleet vs. owner-operators
“Understanding the competition a firm faces within its industry allows positioning the where competition is weakest.”
Applying Industry Analysis (continued…)
Strategies to Alter Industry Structure
Identify key structural features of an industry that are responsible for reducing profitability.
Consider which of those features can positively change through appropriate strategic initiatives
Example: Airline’s Hub-and-Spoke model
Example: American Medical Association
(AMA)’s barriers to enter medical field
“The basis for an industry’s intensity of competition and level of profitability provide opportunities for change by reducing competition.”
Key Issues and Challenges
Five Forces Model
Too Simplified???
Any evidence???
Flawed???
Defining the Industry
Identify the Key Elements of the Industry’s Structure
Producers, Customers, Suppliers
Substitutability
Geographical boundaries - national versus global
Choosing an Appropriate Level of Analysis
Identify Possible Segmentation Variables
Choices about which customers to serve and what to offer them
Construct a Segmentation Matrix
Choose the most important variables
Analyse Segmentation Attractiveness
Identify Key Success Factors in Each Segment
Analyse buyers’ purchase criteria
Analyse the Attraction of Broad Versus Narrow Scope
Continued...
Substitutes and Complements
Schumpeter’s Process of Creative Destruction
Established industries
“Sluggish”
Highly persistent profits
Hypercompetition
Makes the industry less stable
Superior profitability
Key Success Factors
Two Questions:
1. What do our customers want?
2. What does the firm need to do to survive competition?
Resources
Content http://www.slideshare.net/mtmexperience/strategy-analysis-touroperators http://www.netmba.com/strategy/pest/
Images http://sagamer.co.za/img/evolution-phone.jpg