The Structural Analysis of Industries
advertisement
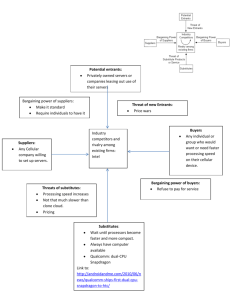
Masters in Engineering and Management of Technology Masters in engineering Design Introduction to Entrepreneurship and New Venture Creation Rui Baptista The Structural Analysis of Industries What is Strategy? | Distinguishing strategy from tactics: z Strategy is the overall plan for deploying resources to establish a favorable position z Tactic is a scheme for a specific maneuver | Characteristics of strategic decisions: z Important both in the short and long run z Involve a significant commitment of resources z Not easily reversible The Basic Framework of Strategy: the Link Between the Firm and Its Environment THE FIRM Goals & Values Resources & Capabilities Structure & Systems STRATEGY STRATEGY THE INDUSTRY ENVIRONMENT Competitors Customers Suppliers Analyzing the Industry Environment OUTLINE | The objectives of industry analysis | From environmental analysis to industry analysis | Industry & market boundaries | Porter’s Five Forces Framework | Applying industry analysis | Extending the Five Forces Framework: Complements, Dynamics, The New Economy | Identifying Key Success Factors Objectives of Industry analysis | To understand how industry structure drives competition, which determines the level of industry profitability. | To assess industry attractiveness | To use evidence on changes in industry structure to forecast future profitability | To identify opportunities to change industry structure to impose industry profitability | To identify Key Success Factors From Environmental Analysis to Industry Analysis The national/ international economy Technology Government & Politics The natural environment THE INDUSTRY ENVIRONMENT • Suppliers • Competitors • Customers Demographic structure Social structure •The Industry Environment lies at the core of the Macro Environment •The Macro Environment impacts the firm through its effect on the Industry Environment Drawing Industry Boundaries: Identifying the Relevant Market | What industry is BMW in: z World Auto industry? z European Auto industry? z World luxury car industry? | Key criteria: GEOGRAPHY and SUBSTITUTABILITY z On the demand side : • Where are the buyers located? Are they willing to substitute across countries? • Are buyers willing to substitute between types of cars? z On the supply side : • Where are the manufacturers located? Are they able to switch production across countries? • Are manufacturers able to switch production between types of cars? Determinants of Industry Profitability (Revenues-Costs) 3 key influences: | The value of the product to customers | The intensity of competition | Relative bargaining power at different levels within the value chain The Spectrum of Industry Structures Perfect Competition Oligopoly Duopoly Monopoly Concentration Many firms A few firms Two firms One firm Entry and Exit Barriers No barriers Product Differentiation Homogeneous Product Potential for product differentiation Perfect Information flow Imperfect availability of information Information Significant barriers High barriers Porter’s 5 Competitive Forces Framework SUPPLIERS Bargaining power of suppliers INDUSTRY COMPETITORS POTENTIAL Threat of ENTRANTS new entrants Threat of SUBSTITUTES Rivalry among existing firms substitutes Bargaining power of buyers BUYERS Threat of Potential Entrants New entrants’ threat to industry profitability depends upon the height of barriers to entry. The principal sources of barriers to entry are: z z z z z z z Capital requirements Economies of scale Absolute cost advantages Proprietary product differentiation (e.g. brand identity) Access to channels of distribution Government Policies: legal and regulatory barriers Threat of retaliation Threath of Substitutes Extent of competitive pressure from producers of substitutes depends upon: z z z z Switching costs Buyers’ propensity to substitute Price-performance characteristics of substitutes Network externalities Bargaining Power of Buyers Buyer’s price sensitivity Relative bargaining power • Switching Costs • Cost of purchases as % of buyer’s total costs • How differentiated is the purchased item? • How intense is competition between buyers? • How important is the item to quality of the buyers’ own output? • Size and concentration of buyers vs. sellers • Buyer volume • Buyer’s information • Ability to backward integrate Note: analysis of supplier power is symmetric Rivalry Between Incumbents (Established Competitors) The extent to which industry profitability is depressed by aggressive price competition depends upon: z z z z z z Industry growth – product/technology life cycle Concentration (number and size distribution of firms) Diversity of competitors (differences in goals, cost structure, etc.) Product differentiation Excess capacity and exit barriers Cost conditions • Extent of scale economies • Ratio of fixed to variable costs Applying 5 Forces Analysis Forecasting Industry Profitability z z Past profitability is a poor indicator of future profitability If we can create of foresee changes in industry structure we can induce changes on competition and profitability Strategies to Improve Industry Profitability • What structural variables affect profitability? • Which of those variables can be changed by individual or collective strategies? Entrepreneurial Industry Evaluation Factors Attractiveness High Low Competition among companies Competition is minimal but will become intense in a year The industry is mature or declining Power of customers Volume is high and willing to negotiate Customer has few switching costs Power of suppliers Many substitutes and sources are available Limited supply; differentiated products Entry Complex barriers and high entry costs Many start-ups attempting to enter Few, simple entry barriers Few companies are entering this market Complement Complementary products being introduced with high demand growth Dominant companies control market for complementary products Entrepreneurship and Dynamic Competition Porter’s framework assumes: • • industry structure drives competitive behavior Industry structure is stable But competition also changes industry structure Schumpeterian Competition: A “perennial gale of creative destruction” where innovation overthrows established market leaders Hyper-competition: intense and rapid competitive moves, creating disequilibrium through continuously creating new competitive advantages and destroying, neutralizing or making obsolete opponents’ competitive advantages—overlapping product/technology life-cycles Applying the 5 Forces to Digital/E-Business Markets • The more unstable is industry structure—the less helpful is analysis based upon industry structure • Taking account of time—willingness to endure losses today in order to reap profit tomorrow • General structural features of digital, networked industries: Low Entry Barriers + Extreme Scale Economies + Network Externalities = = Winner-take-all markets = Intense competition Porter’s Framework in the Knowledge Economy SUPPLIERS Bargaining power of suppliers Network externalities: the suppliers of complements create value for the industry and can exercise bargaining power INDUSTRY COMPETITORS POTENTIAL Threat of ENTRANTS new entrants Threat of SUBSTITUTES Rivalry among existing firms substitutes Bargaining power of buyers BUYERS Identifying Key Sucess Factors Pre-requisites for for success Pre-requisites success What do customers want? How may the firm survive competition? Analysis of competition Analysis of demand • Who are our customers? • What do they want? • What drives competition? •• What What drives are thecompetition? main • What are theof main dimensions competition? dimensions of competition? •• How How intense intense is is competition? competition? •• How How can can we we obtain obtain aa superior superior competitive competitive position?position? KEY SUCCESS FACTORS Entrepreneurial Industry Evaluation Factors Rivalry/Competition Costumer Power Supplier Power Barriers to Entry Substitute and Complementary Products Attractiveness High Low